Unveiling the Booming GIS Trends in 2024
Navigating the Geospatial Revolution – Top GIS Trends in 2024
The world of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is witnessing an era of exceptional growth and innovation as we step into 2024. The multifaceted applications of GIS technology are leaving notable imprints across diverse sectors, and the upcoming year is poised to witness a surge in its utilization. Let’s explore the sectors where GIS is set to make significant strides in 2024.
1. Governmental Developmental Activities
In the realm of governmental activities, GIS has become increasingly indispensable for numerous developmental initiatives, ranging from urban planning to infrastructure development. Globally, governments are leveraging GIS to make well-informed decisions. In the context of the Digital India Mission, there has been a significant digital transformation, encompassing the digitization of district plans, town plans, road and rail networks, as well as the integration of land information with Record of Rights (ROR) data.
This digital revolution extends to various departments, including disaster management, safety, and defense. The following screenshot exemplifies various departments, harnessing advanced GIS and Remote Sensing technologies for detailed analyses, policy-making, and decision-making activities as a part of the smart city mission. Based on past applications and implementations, it is anticipated that in 2024, this trend will continue to soar higher. GIS is expected to play a crucial role in efficient resource allocation, disaster management, and optimizing public service delivery. The direction suggests a continual and increased dependence on GIS to enhance governance and improve decision-making processes.
2. Access to Open Source Moderate/ High-Resolution Earth Observations
In 2024, the increased availability of Open Source Moderate/ High-Resolution Earth Observations datasets is set to transform GIS applications across various sectors, encompassing environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster management, agriculture, infrastructure development, natural resource management, humanitarian aid, and wildlife conservation. These expanded data access points will empower researchers engaged in diverse research and developmental activities, recognizing the importance of thorough research for effective policy implementation and developmental initiatives.
The significance of high-resolution imagery cannot be overlooked, as it plays a critical role in studying environmental changes, optimizing urban layouts, improving disaster response, and advancing precision farming. These imageries support accurate assessments in infrastructure development and contribute to sustainable resource management.
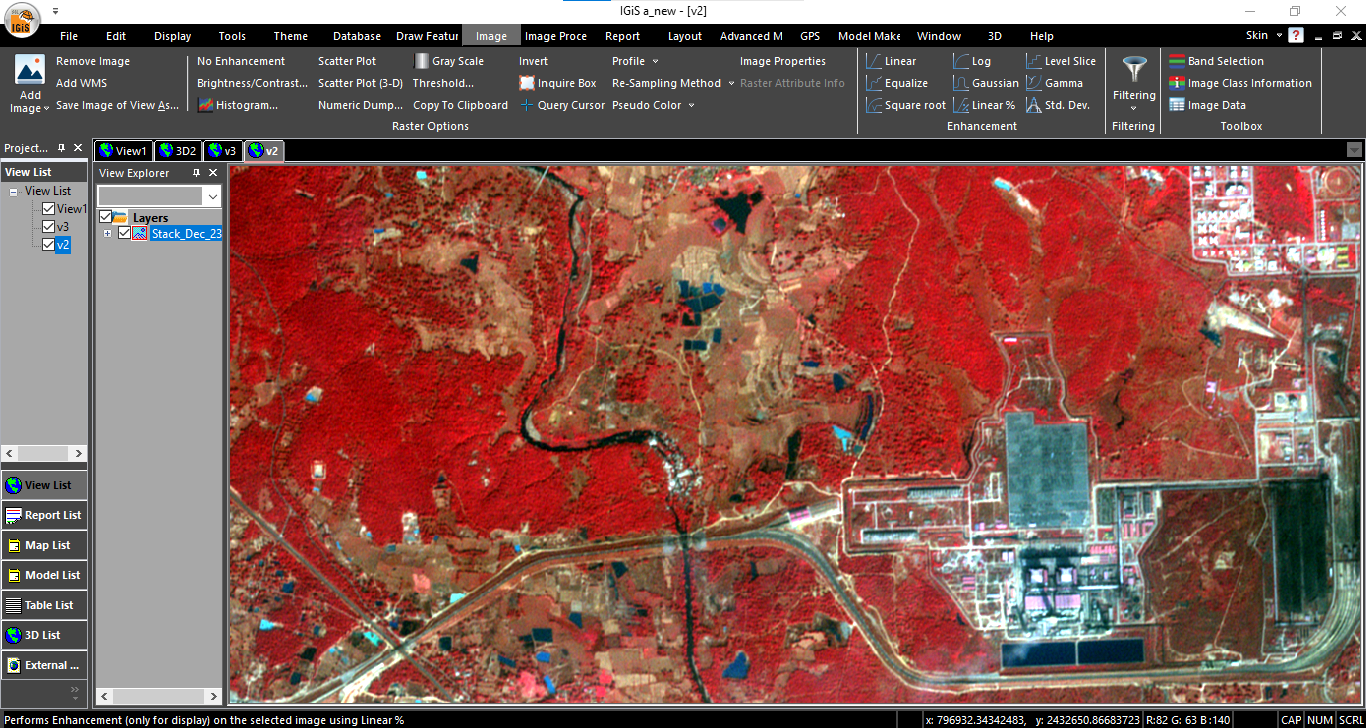
This evolving trend represents a significant move towards a more accessible and expansive geospatial data environment, particularly after ISRO started offering free access to all its data repository up to 5.4m spatial resolution satellite imagery of the Indian Subcontinent. By delivering timely and accurate information to decision-makers in vital sectors, this advancement is poised to greatly improve their capacity for making well-informed decisions in 2024.
3. Integration of Attribute Information with Locational Intelligence
Amidst the progressing landscape of GIS technology in 2024, the combination of Attribute Information with Locational Information stands out as a pivotal advancement. This integration significantly amplifies comprehensive analysis, impacting diverse aspects such as urban development, infrastructure management, project initiation to execution reporting, optimized traffic management, the implementation of safe city projects, and several other applications. As governmental departments increasingly embrace GIS technology for enhanced management and planning activities, the integration of relevant information with geographic location adds a layer of advanced insight to these crucial activities. This collaboration is vital in providing decision-makers with a more refined understanding of spatial relationships, fostering improved planning, streamlined execution, and heightened efficiency in the dynamic field of GIS advancements in 2024.
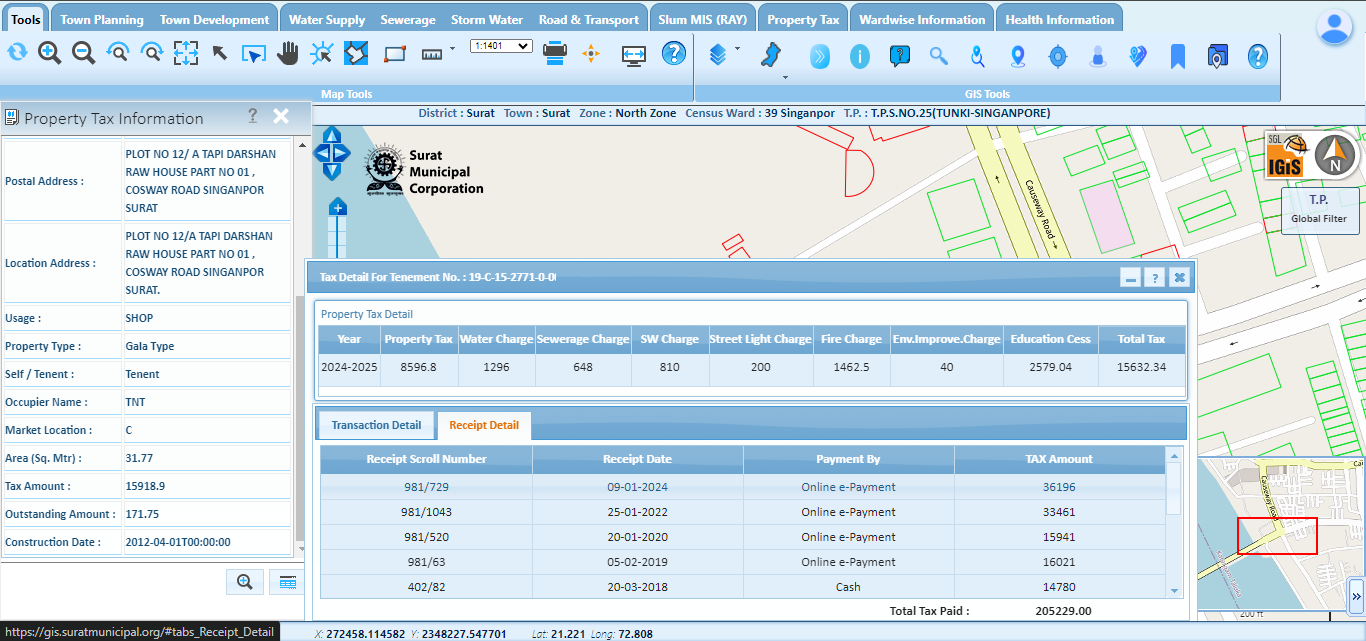
So, as discussed, the rapid expansion of attribute information, combined with its integration into locational intelligence is fundamentally changing our approach to data utilization. An illustrative example is the integration of advanced GIS solutions with property tax departments, which offers detailed attribute information alongside location mapping. This integration provides valuable insights for enhanced planning, monitoring, and maintenance of systems. Looking ahead to 2024, the fusion of attribute data, including demographics and socio-economic factors, with spatial information, is poised to drive advanced analytics. This integration will support businesses and organizations in targeted marketing, customer profiling, and strategic decision-making, ushering in a new era of data-driven insights and efficiency.
4. IoT Sensor Integration for Real-Time Data Updates
The integration of GIS with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors emerges as a transformative force in real-time data acquisition and analysis. In 2024, this trend is expected to thrive, facilitating the collection of live, location-based data. Enterprise-based GIS systems seamlessly integrate information obtained from IoT sensors, emphasizing the significance of combining collected data with its locational insights. The implications of this integration extend across industries, offering numerous examples of how IoT sensors can contribute to technological advancements.
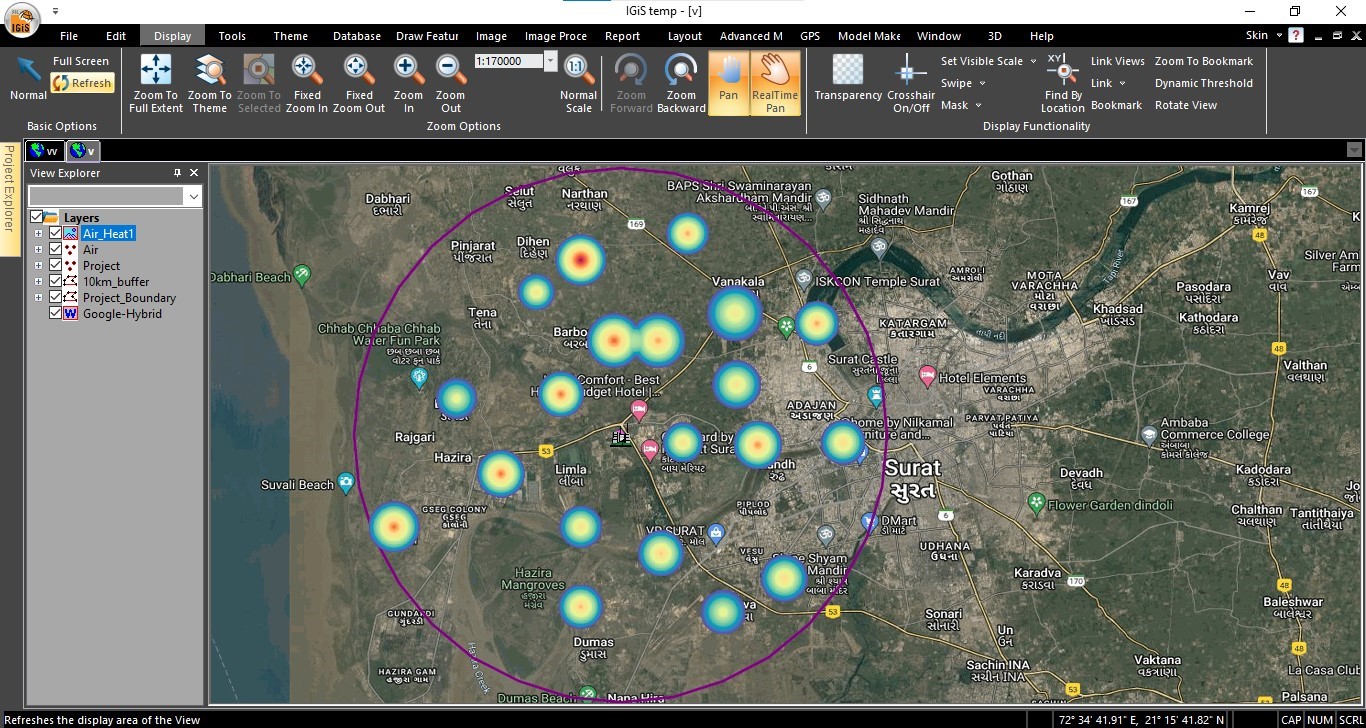
By combining data from IoT sensors with the spatial context provided by GIS, organizations gain a powerful tool for data-driven real time decision-making. This synergy enhances the efficiency of monitoring various infrastructures and environmental conditions. For instance, in utility services, such integration enables immediate updates on water and gas supply information.
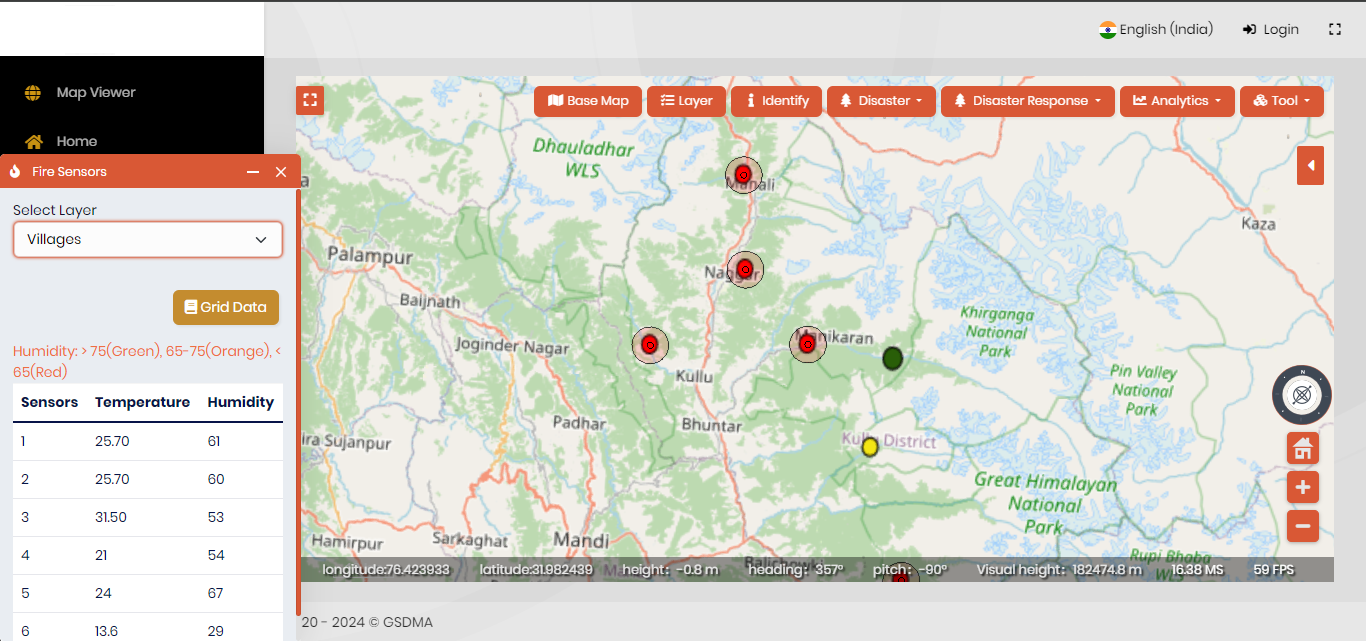
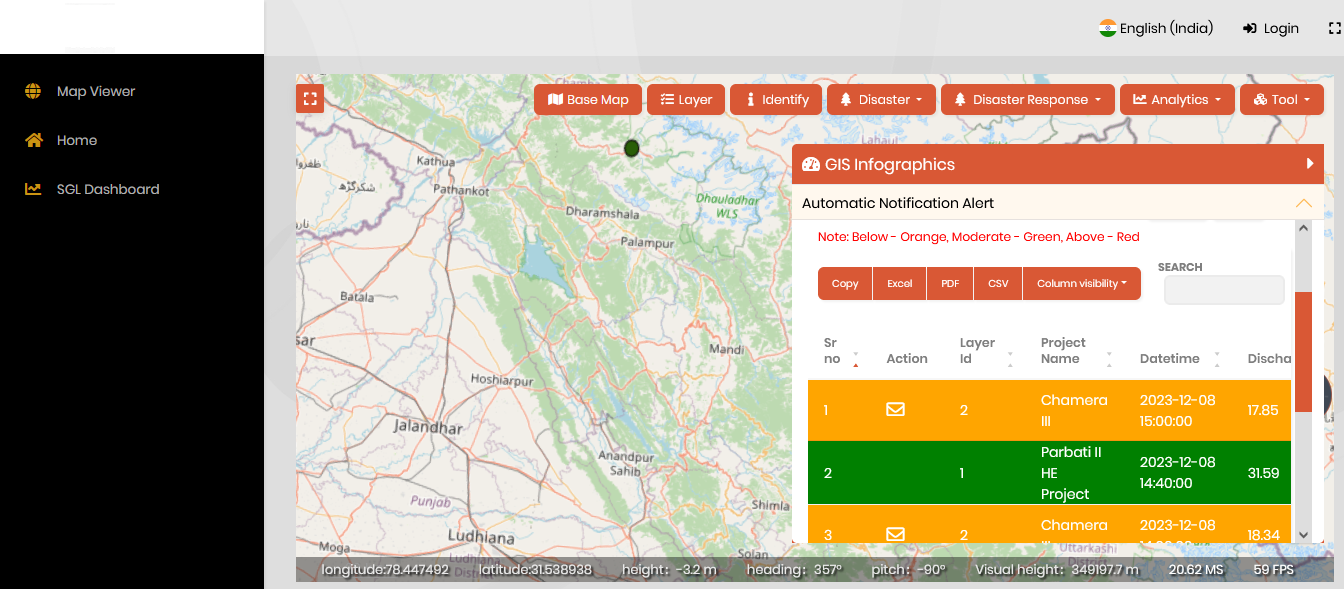
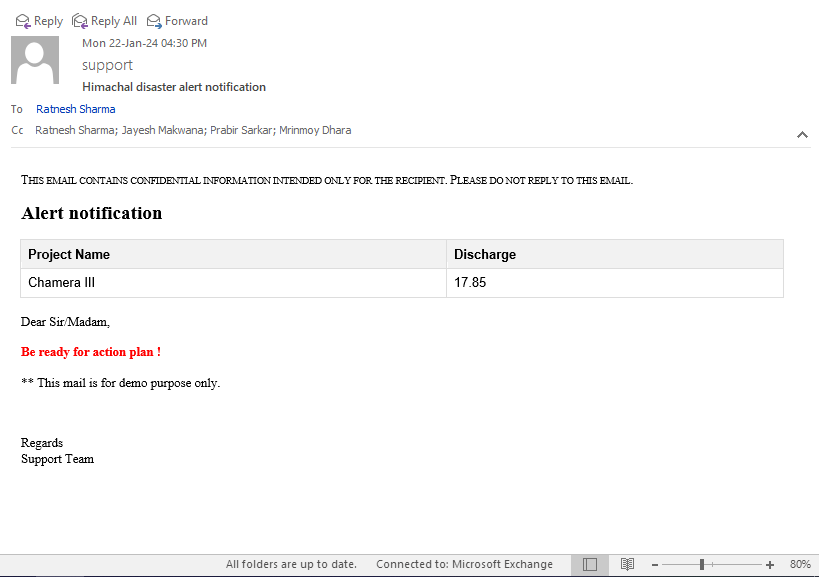
Additionally, environmental factors like pollution, weather conditions, and flood monitoring can be continuously monitored. The GIS platform not only visualizes this sensor-generated data on a map, but it can also generate alerts when the permissible limits are crossed along with the comprehensive and geospatially accurate view. This not only facilitates enhanced monitoring but also streamlines maintenance activities, contributing to more informed and efficient management across industries. The integration of IoT sensors with GIS systems represents a crucial step towards achieving greater connectivity, precision, and effectiveness in leveraging spatial data for improved decision-making processes.
5. Application of AI/ ML technology in GIS
The application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technology in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Remote Sensing is revolutionizing data analysis and interpretation. AI/ML algorithms are proficient at processing vast datasets, extracting meaningful patterns, and automating complex tasks in GIS and Remote Sensing applications. In 2024, this integration allows for enhanced analysis by enabling automatic feature extraction, object detection, and classification of geographic data. These technologies bring a new level of efficiency to tasks such as land cover classification, change detection, and image interpretation using various advanced machine learning algorithms, such as RCNN, Faster RCNN, etc. AI/ML also contributes to predictive modeling, allowing for more accurate forecasting of environmental changes and natural phenomena. The synergy between AI/ML and GIS not only accelerates data processing but also augments the capability to derive valuable insights from spatial information, fostering advancements in environmental monitoring, urban planning, agriculture, and disaster management.
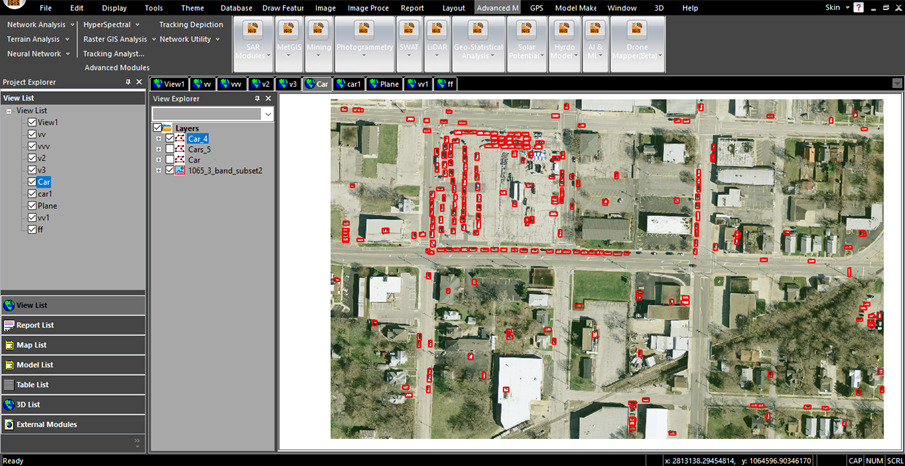
6. Rising Human Awareness
In contemporary society, there is a growing awareness and acceptance of GIS technology among the general population. People are actively incorporating GIS into their daily lives, utilizing location-based services on smartphones, and participating in crowdsourced mapping initiatives. This heightened engagement reflects an acknowledgment of the power and significance of GIS in providing spatial information. In 2024, this trend is anticipated to persist and even escalate, indicating a continuous upward trajectory. The result is a society that is increasingly geospatially aware, with individuals recognizing and appreciating the practical applications and benefits of GIS technology in various aspects of their daily routines.
Conclusion
As we approach the year 2024, the GIS landscape is brimming with promise and potential across sectors. The integration of technology with geographic information continues to redefine how we interact with our surroundings and make crucial decisions. From government-led developmental activities to the conscious use of location-based data by individuals, the year ahead promises a vibrant evolution in GIS applications.
In the thriving landscape of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), IGiS stands out as a vital indigenous platform, offering essential support for diverse GIS and Remote Sensing analyses. This robust platform provides advanced technological capabilities, including routing and planning features, terrain analysis for 3D modeling, SAR Data Processing, etc. By encompassing a range of sophisticated functionalities, IGiS plays a pivotal role in empowering professionals and organizations engaged in GIS activities through its end-to-end enterprise-level solution. Its diverse set of tools enhances the efficiency of spatial analysis and modeling, contributing significantly to the booming industry of GIS by providing a versatile and indigenous solution for a wide array of geospatial applications.
Stay tuned & use IGiS, as GIS takes center stage in shaping our world, providing innovative solutions and insights that transcend boundaries and revolutionize the way we perceive and utilize spatial information.
Latest Blog

Smart Waste Management with GIS
1. Introduction: Waste management entails the responsible collection, processing, and disposal of waste materials with a focus on environmental preservation. Its core objectives include waste reduction, resource recovery, and the....
Read More