POWER OF GIS TO EMPOWER SMART CITY MANAGEMENT
In India, the 100 Smart Cities Mission was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on June 25, 2015, to enhance the citizen’s lifestyle through user-friendly sustainable and smart technologies. Additionally, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi kick started two more significant initiatives namely ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Make in India’. These initiatives have digitally expanded and strengthened economic growth. The smart city mission is one of them.
The smart city concept embraces optimization and efficacy of the services & operational activities of the city municipal corporation and includes easy communication with the citizens by sharing the information. ICT (Information and Communication Technology) is the cutting edge technology adopted for delivery of excellent government services & citizen welfare.
The better quality of life for the citizens, is driven with a purpose of being supportable, robust, and approachable through adoption of smart solutions for different public services like transportation, healthcare emergencies, education, water supply & sanitation infrastructure, tourism, telecommunications, and every other service with impacts the liveable fabric of the citizens including Public administration and governance.
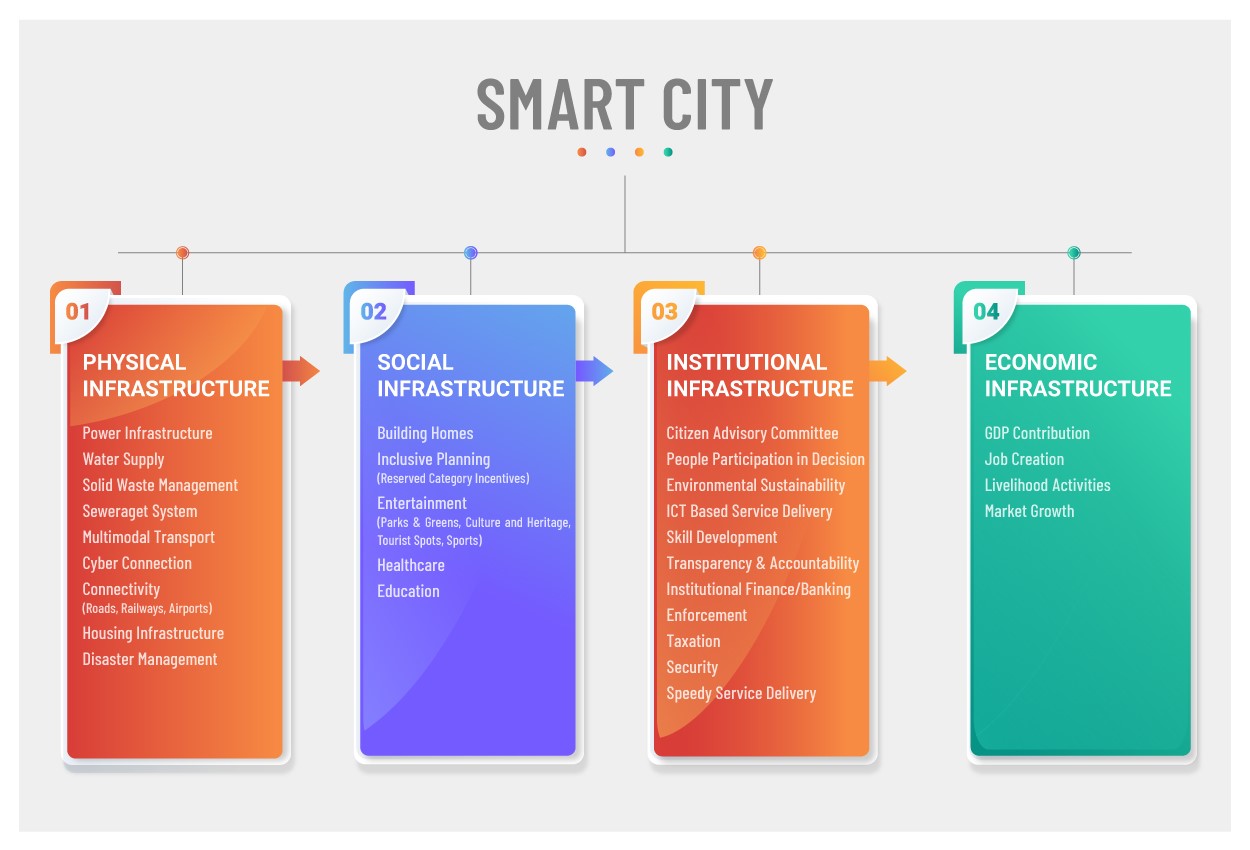
Before knowing the role of technology in the smart city concept, we have to know the definition and concept of a smart city. It is based on four pillars: Social Infrastructure, Physical Infrastructure, Institutional Infrastructure (including Governance) and Economic Infrastructure. Each pillar is more focused on the citizens’ welfare. The social infrastructure gives information about physical facilities & where the people can access social services. The physical infrastructure provides the facilities about the utility services. Similarly, Institutional Infrastructure (including Governance) and Economic Infrastructure facilitate citizens’ lives in a better way.
The main objective of a smart city is to optimize city functions & encourage economic growth with a clean & sustainable environment while also enhancing a decent quality of life for citizens by using smart technologies and data analysis.
As we discussed earlier, Information and Communication Technology (ICT) has been used to make a city Smart by solving city/urban challenges. The significance of the technology lies not in the number of technologies available, but in how it is used to empower citizens. At the world level, the key to the growth of smart cities is not only ICT but also other advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Geospatial Technology.
Nowadays, GIS for smart cities has become an essential part of our daily lives. GIS also gives an IT infrastructure that includes not only every stakeholder but also every activity (starting from planning & conceptualization to development & maintenance) of the smart city. It enables to collect the location-based data as well as maintain the spatial database and confirms a seamless flow of information/data and links to the requirements of various stakeholders.
Geospatial Technology i.e., GIS, Remote Sensing, and GPS primarily plays a vital role in the implementation of Smart City activities. There are many GIS products for smart cities to implement smart city projects or activities. But IGiS (Integrated GIS & Image processing Software) is an integrated platform for GIS analysis, Image Processing, Photogrammetry, and CAD under the Make in India Initiative. IGiS is jointly developed by Scanpoint Geomatics Limited (SGL) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
IGiS empowers the city‘s utility assets management effectively & improves the participation of the citizens. IGiS is a single platform that offers end-to-end geomatics solutions that can provide geo-enabled services to the different components of smart city applications.
GIS applications in smart cities are numerous and SGL has successfully completed many smart city projects. A few significant applications of IGiS in smart city projects with screenshots are depicted below.
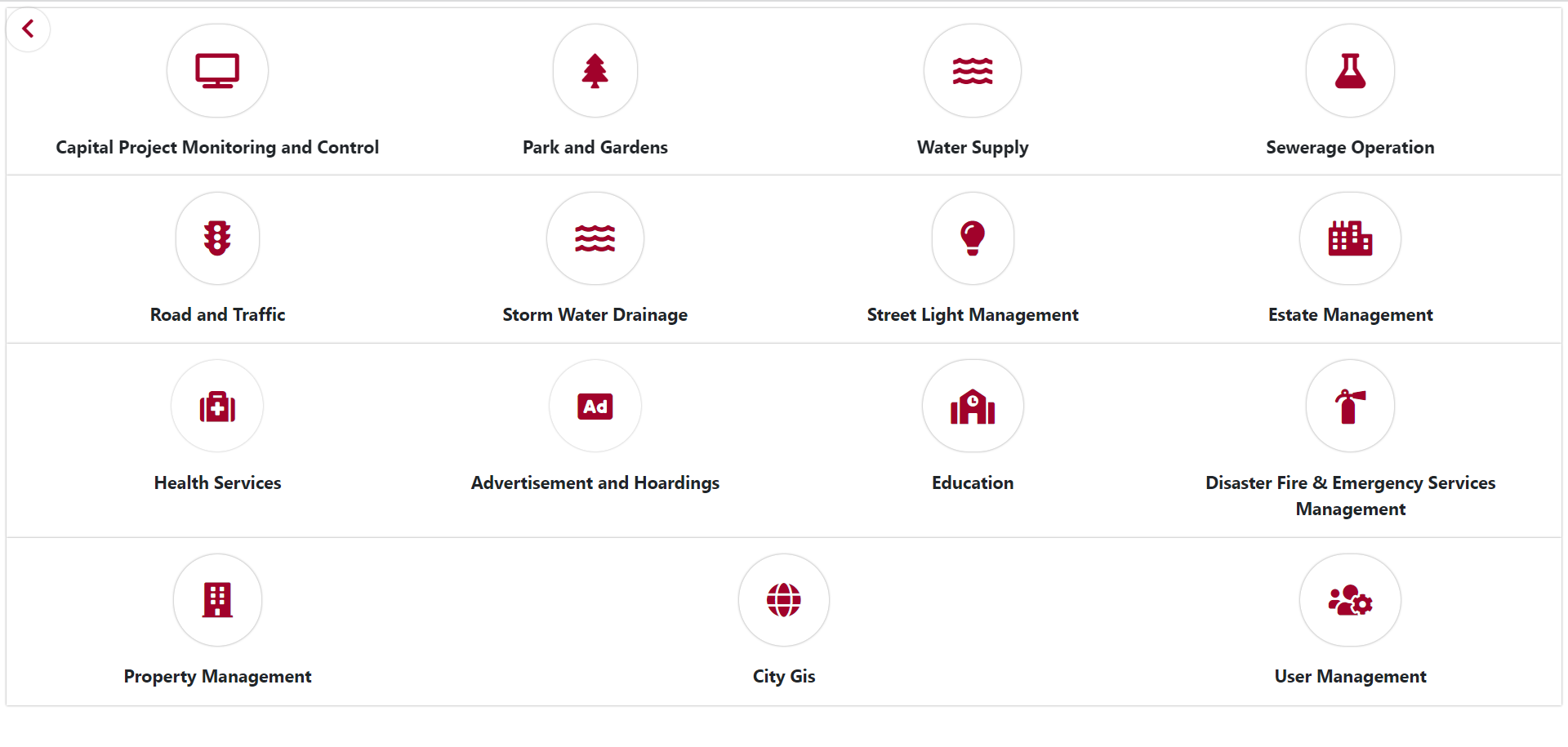
Image Source: Agra Smart City – http://117.211.200.134:7413/Home/Portal/DepartmentPage
» 1. GIS used for City Planning
The applications of GIS in smart city planning are countless. The city always has a dense population & more infrastructure but the IGiS tools help the planners to understand the needs of such a city. Also, the planners can adapt to examining smaller towns and slum or informal settlements. IGiS has the capability of performing a variety of queries hence experts can analyze how new planning activities will fit in with the current/ infrastructure and meet regulatory demands.
IGiS offers powerful mapping and advanced visualization tools which are enabling planners to create 3D view of city. The environmental and socioeconomic data can be used to create maps & can perform tasks like:
» Land Acquisition & New Area Development Planning
» Slum Rehabilitation Development Planning
» Development Planning (Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Park, Garden, Health, Education, Vehicle Parking)
» Utility Development Planning (Water, Sewerage, Solid waste, Road, Footpath, Streetlight)
» Suitable Site Selection or Land Suitability Analysis
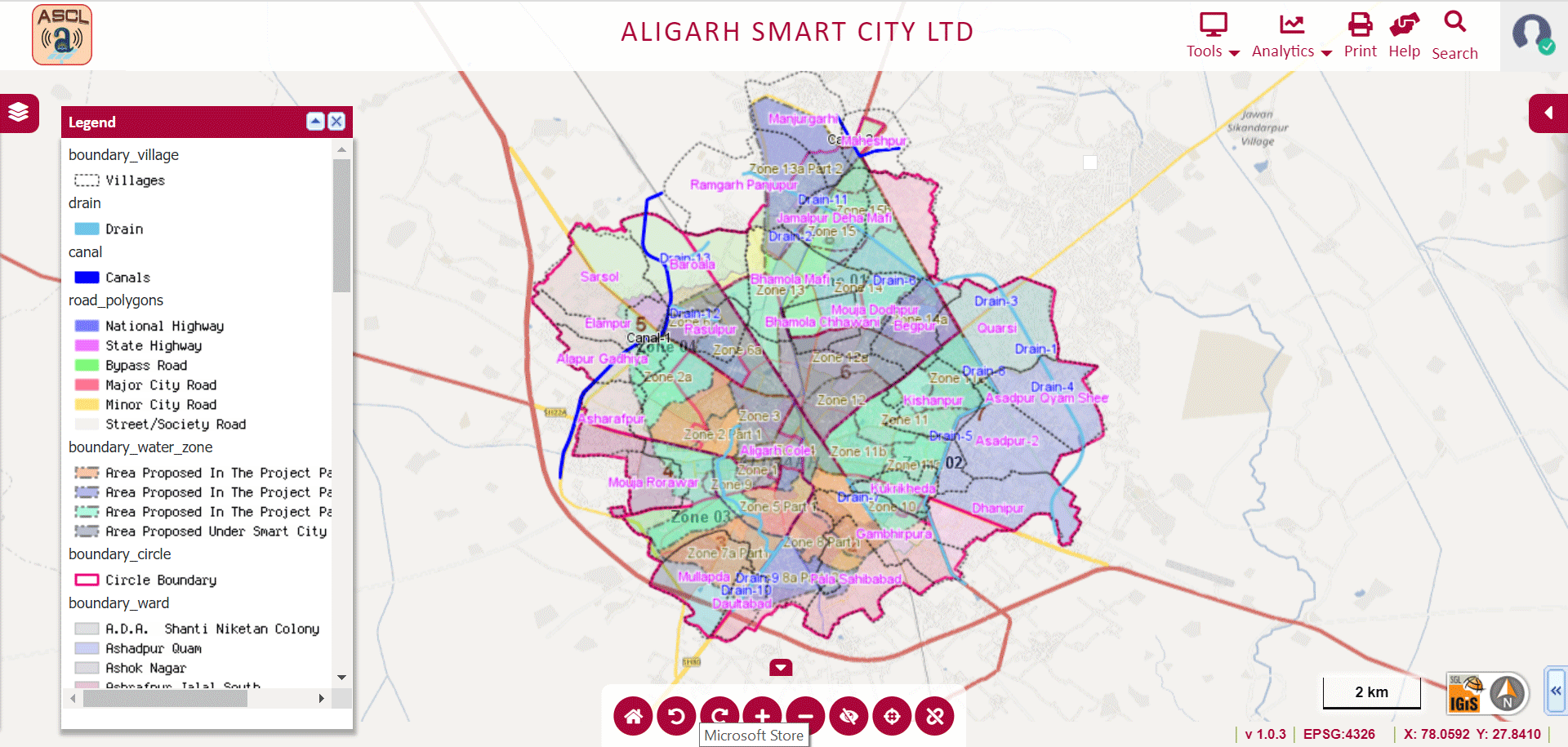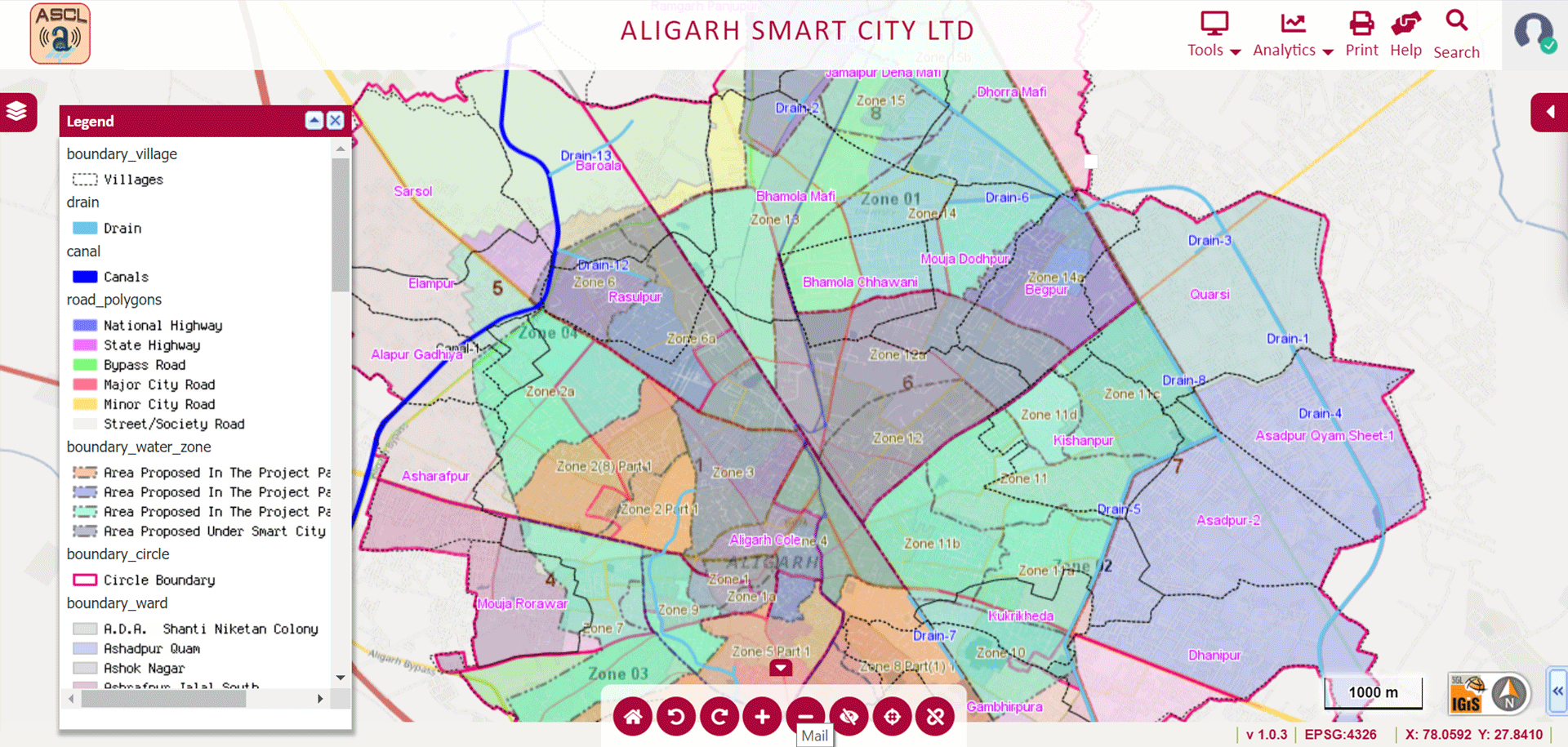
Image Source: Aligarh Smart City – http://gis.nnaligarh.in/GIS/Home/GISPortal#
» 2. Property Tax Analysis using GIS
A GIS platform for Smart City is used to act as the backbone of the geospatial database. IGiS acts as a single platform for handling property information. All properties are geo-enabled. Through the Property Tax Analysis module in IGiS, officials can easily identify the tax defaulters and in the long run government can have exponential growth in revenue. IGiS enables stakeholders to derive information about the property like age of property, type of property (residential, commercial), unpaid taxes, properties converted from residential to commercial & so on. Primary features of the IGiS Property Tax Analysis Module are:
» GIS Based Property Tax Analysis Dashboard
» Integration with Property Tax Management Information System (MIS) Application
» Image Processing based New Property Identification
» Property Tax Defaulter Analysis
» Geo Enabled (location enabled) Support to Revenue Inspectors
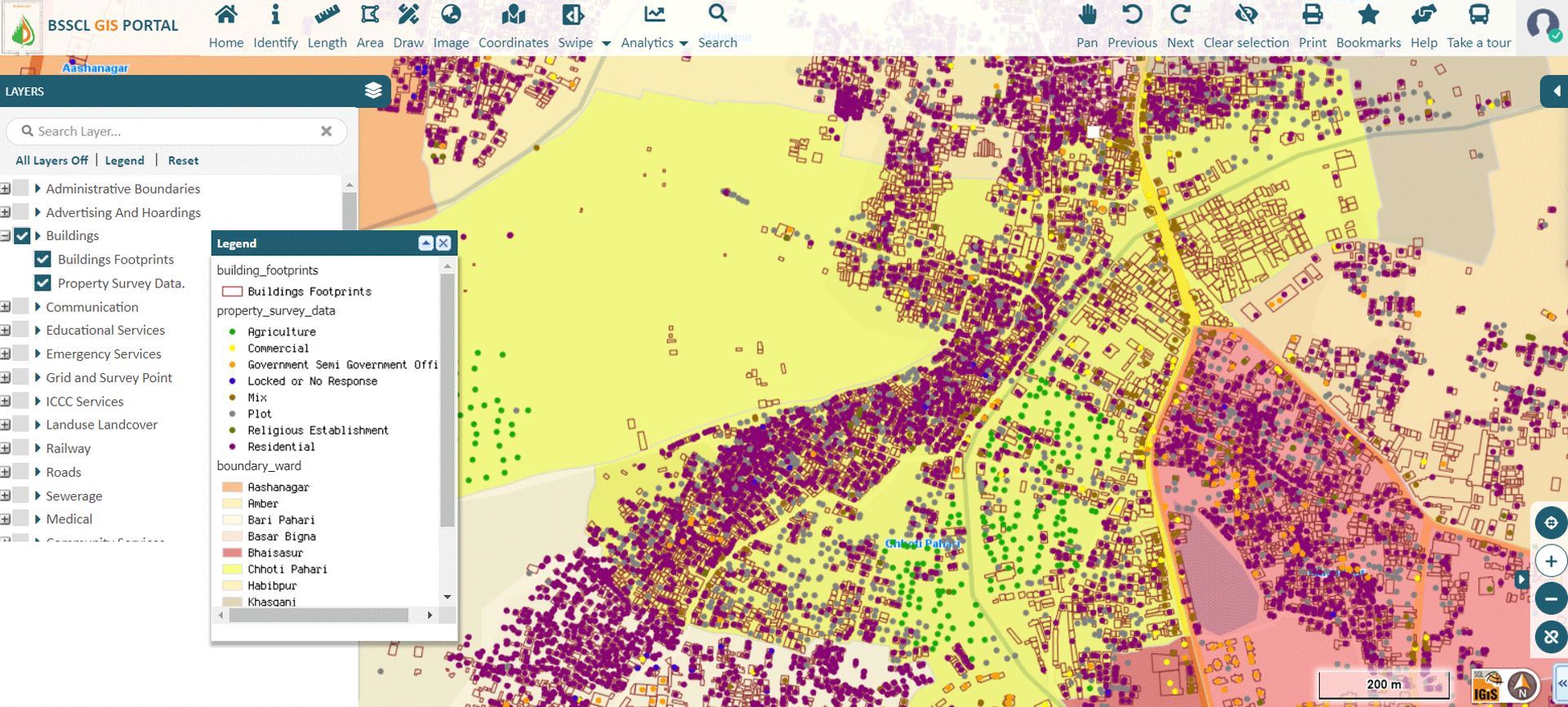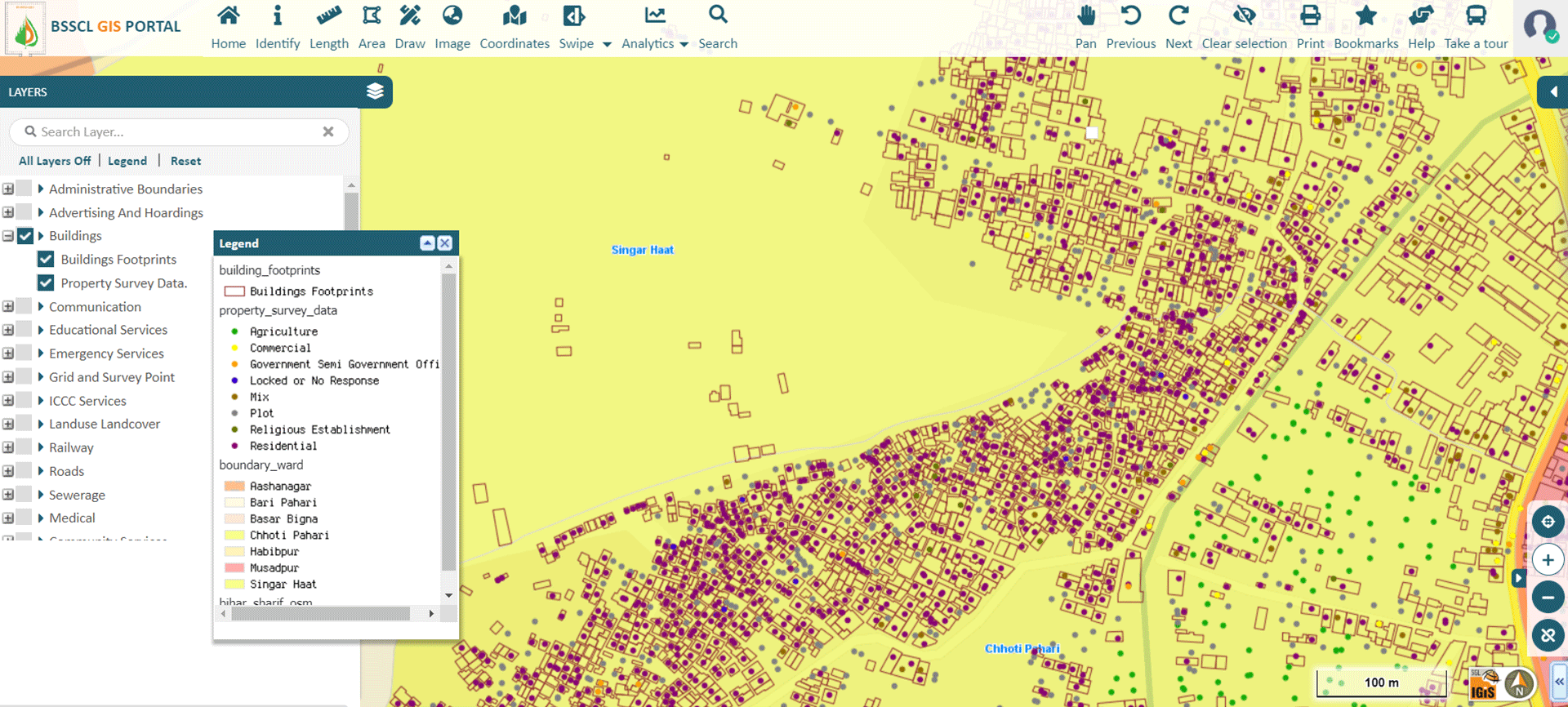
Image Source: Bihar Sharif Smart City – https://gisweb.biharsharifsmartcity.co.in/GIS/Home/GISPortal
» 3. Encroachment Analysis using GIS
GIS provides the optimum solution for Encroachment Analysis. Predominantly GIS can identify encroachment activities like:
» Government Plot Encroachment Analysis & Residential Property Analysis
» Non Compliance with Land Use Encroachment Analysis
» Water Body Encroachment Analysis & Green Coverage Analysis
» Green Cover Encroachment & Illegal Parking Encroachment Analysis
» Geo-tagged Accountability work flow
» Identify the unauthorized Construction Information
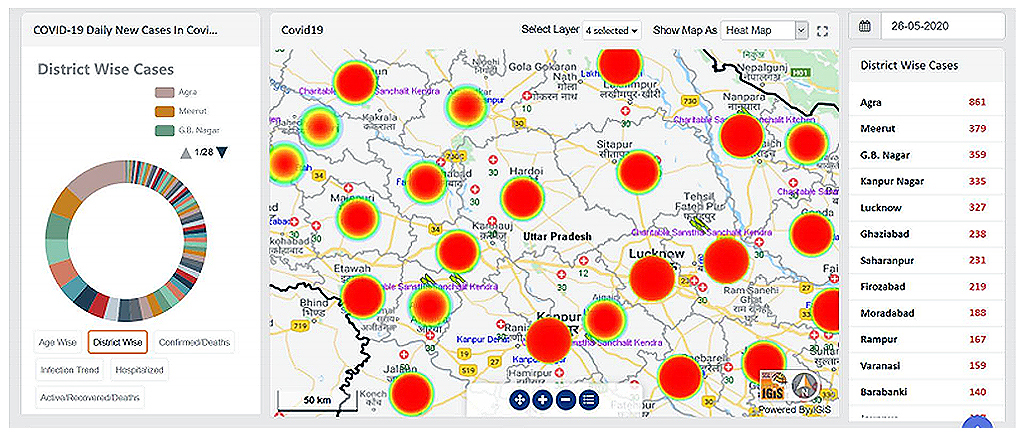
» 4. Health Service Analysis using GIS
The location-based services play a remarkable role to reach the destination of unknown places by using geospatial technology. It will help to access the healthcare facilities (hospitals/clinics, medical stores, rural /primary health centres, and many others). A true example and realized by everyone, IGiS played a significant role to develop the maps regarding pandemic (COVID-19) emergency time.
» 5. Road and Traffic Network Analysis using GIS
The smart technology adoption for transportation systems is now available everywhere with automated signaling, live status of vehicle, live location tracking platform, and many others. Alternative or cost-effective routes can be analysed in case of traffics, emergencies or certain festivals and etc.
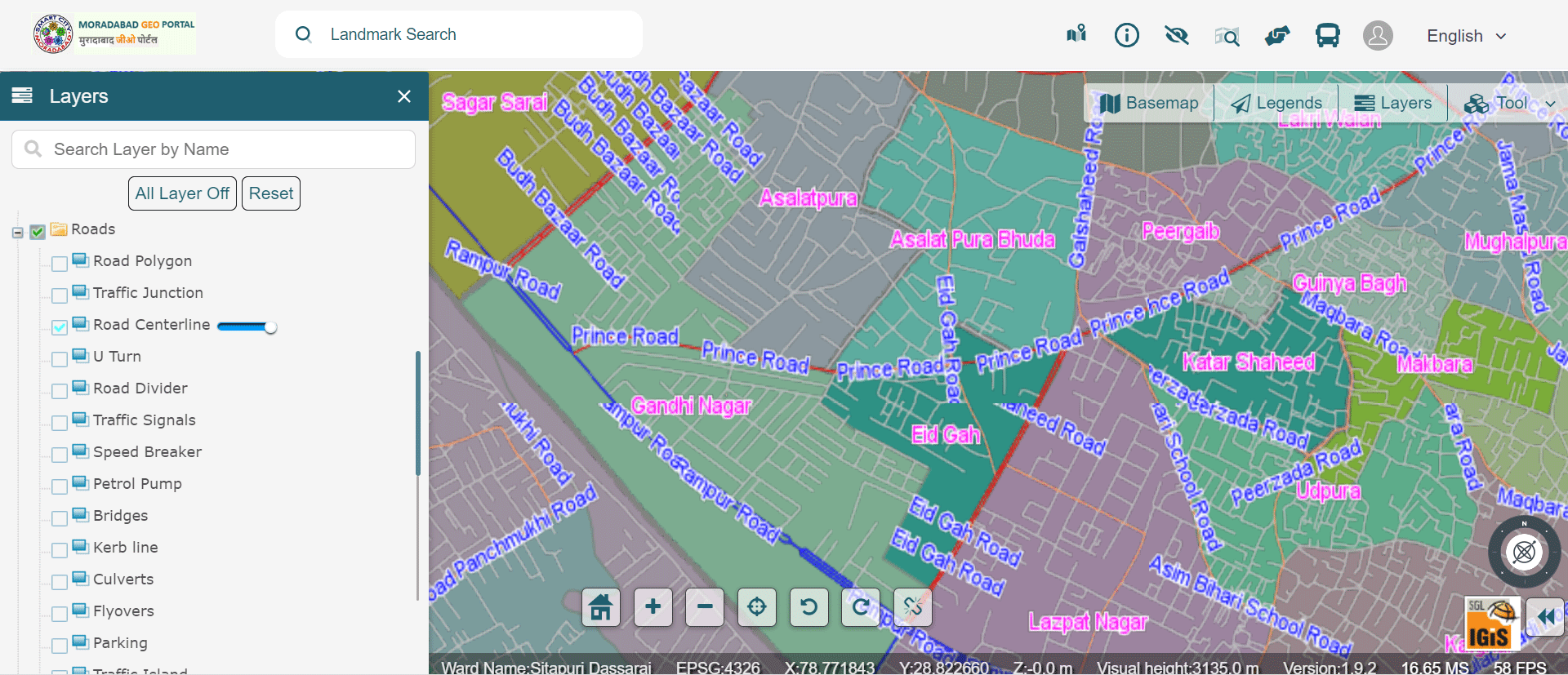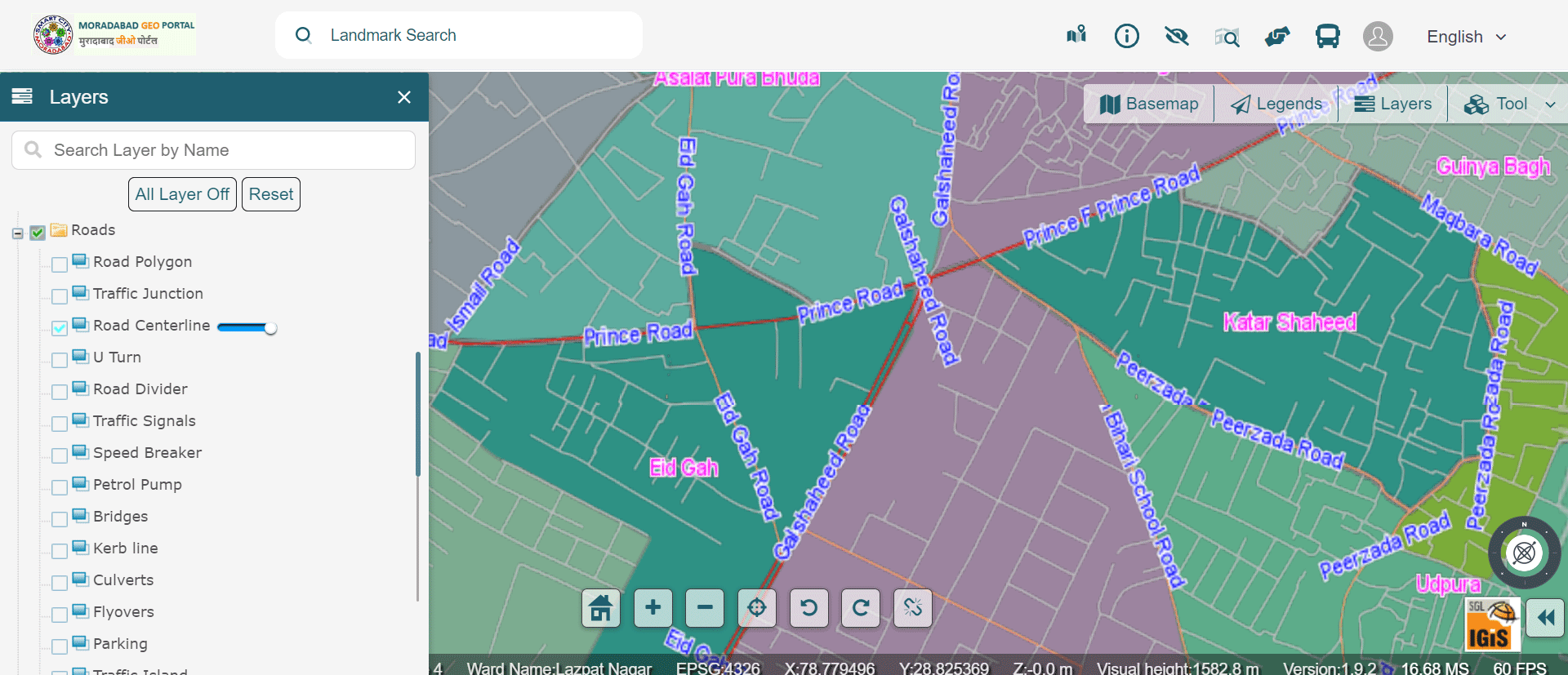
Image Source: Moradabad Smart City – https://gis.smartcitymoradabad.org/gis-portal
» 6. Water Supply Network using GIS
GIS technology is used to view information related to water supply:
» Mains, Distribution Line, Wells, Over Head Tanks, Water Supply Pipeline, Waste Water Supply.
» Public Taps, Storage, Street Taps, Ground Level Dump Reservoir, Direction of Flow, Meters, Consumer.
In addition to this, the water source of the city can be easily identified from different water bodies such as lakes, open wells, bore wells, etc. The shortest route from the particular pumping station to the different distribution networks of water pipelines can be assessed. Using GIS one can plan and track the maintenance schedule of water supply pipes.
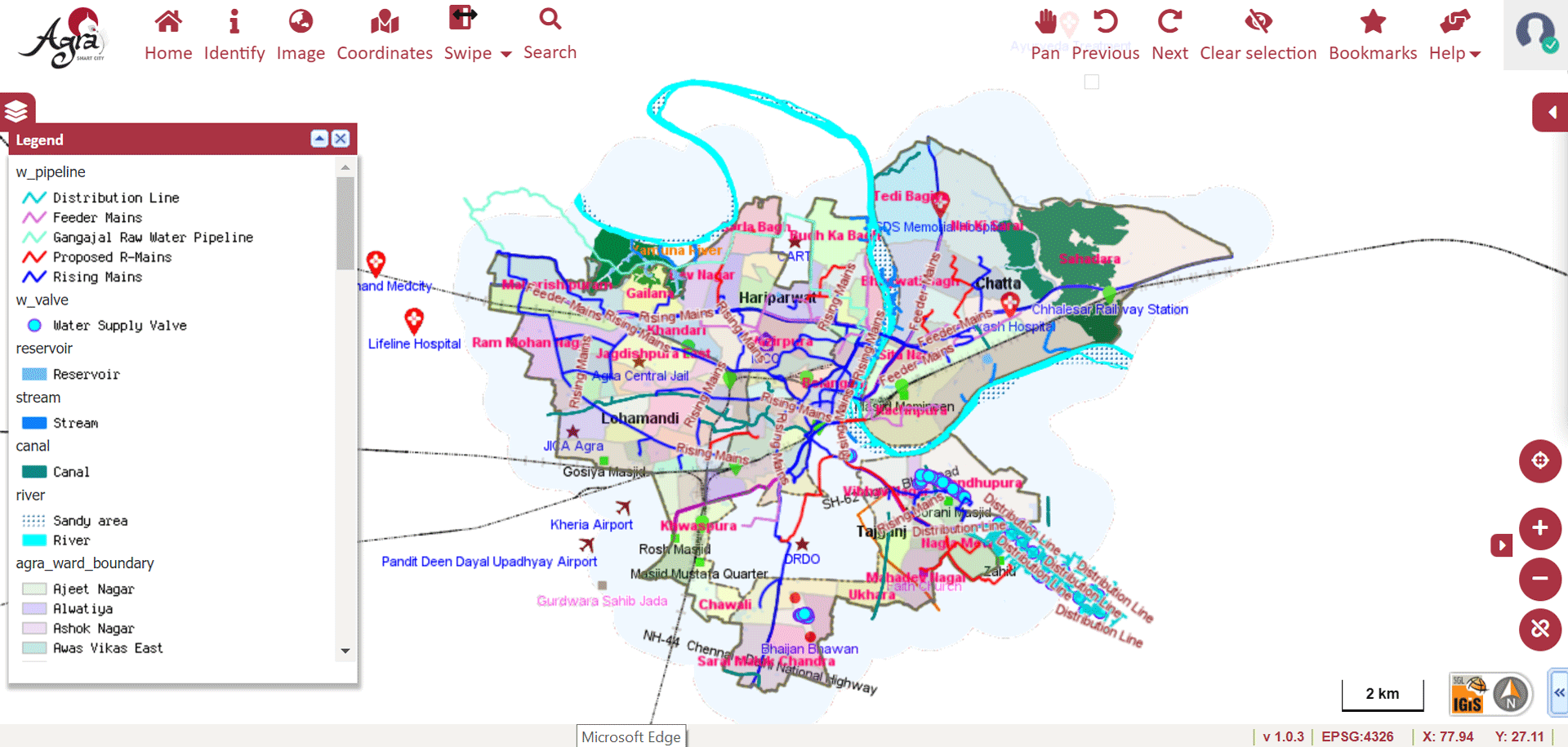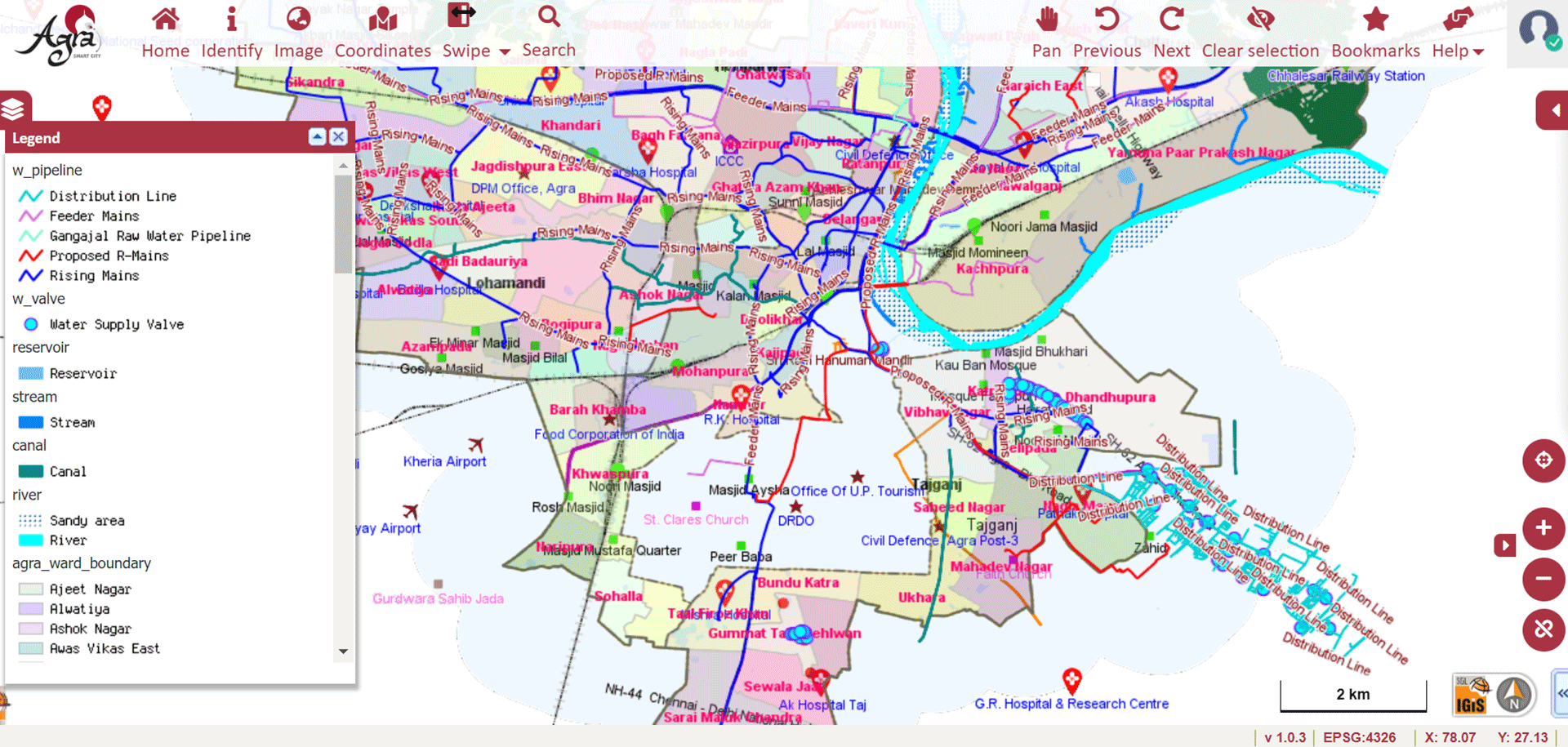
Image Source: Agra Smart City – http://117.211.200.134:7413/GIS/Home/GISPortal#
» 7. Sewerages Network Analysis using GIS
Similar to water supply network analysis, GIS technology is used to plan and track the maintenance schedule of sewerage lines. It is also used to identify the information spatially by query analysis based on many factors (diameter of the pipeline, material of construction, flow capacity, depth of the pipeline). Also, details such as status of pumping mains, current capacity of sewers, dumping sites, transfer stations and waste handling facilities can be digitally ascertained.
The Sewer Network Analysis module graphically displays information on:
» Septic Tanks, House Hold Connection, Pits, Manholes, Open Drainage
» Derivation line of underground pipes using manhole and well locations
» Connectivity of House Hold Network, Flow Direction to be taken up to STP
» Disposal Sites
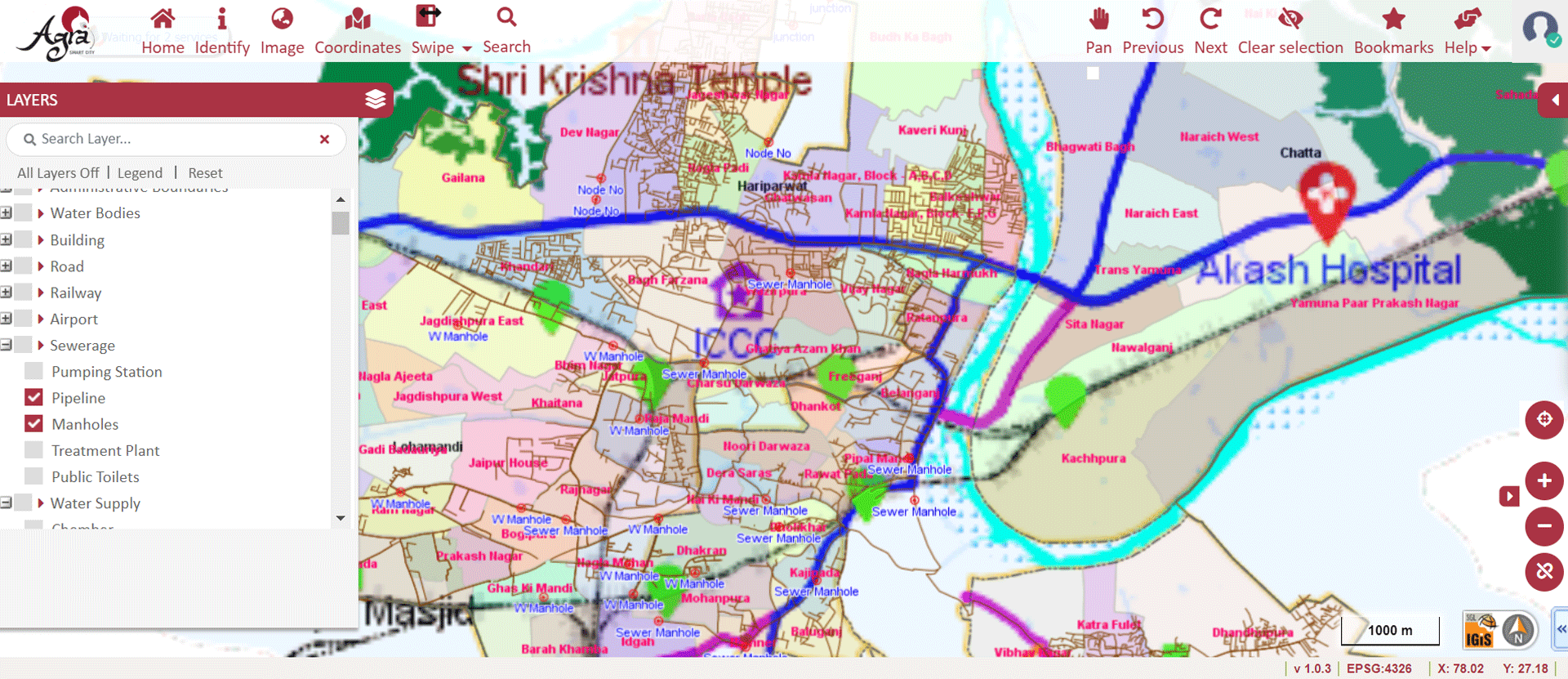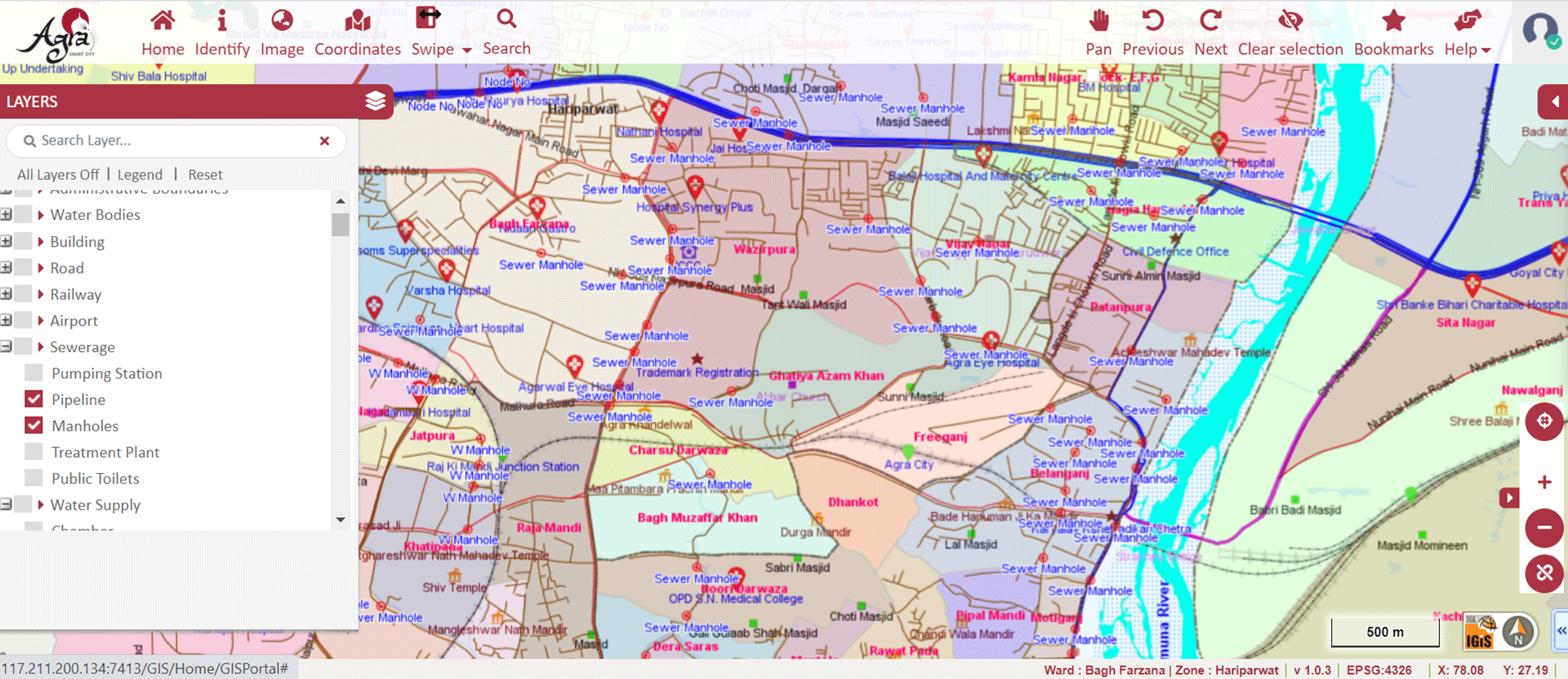
Image Source: Agra Smart City – https://gis.lscl.in/GIS/Home/GISPortal#
» 8. Solid Waste Analysis using GIS
Using GIS technology, we can optimize the route for the waste collection process. It enhances the collection efficiency & officials can track the waste collection process and transportation vehicles. Additionally, we can use the GIS technology for future resource requirements like vehicles & human resources for planning and monitoring of solid waste. In the IGiS Solid Waste Analysis module, officers can plan Dustbin Locations, Garbage Collection, etc.
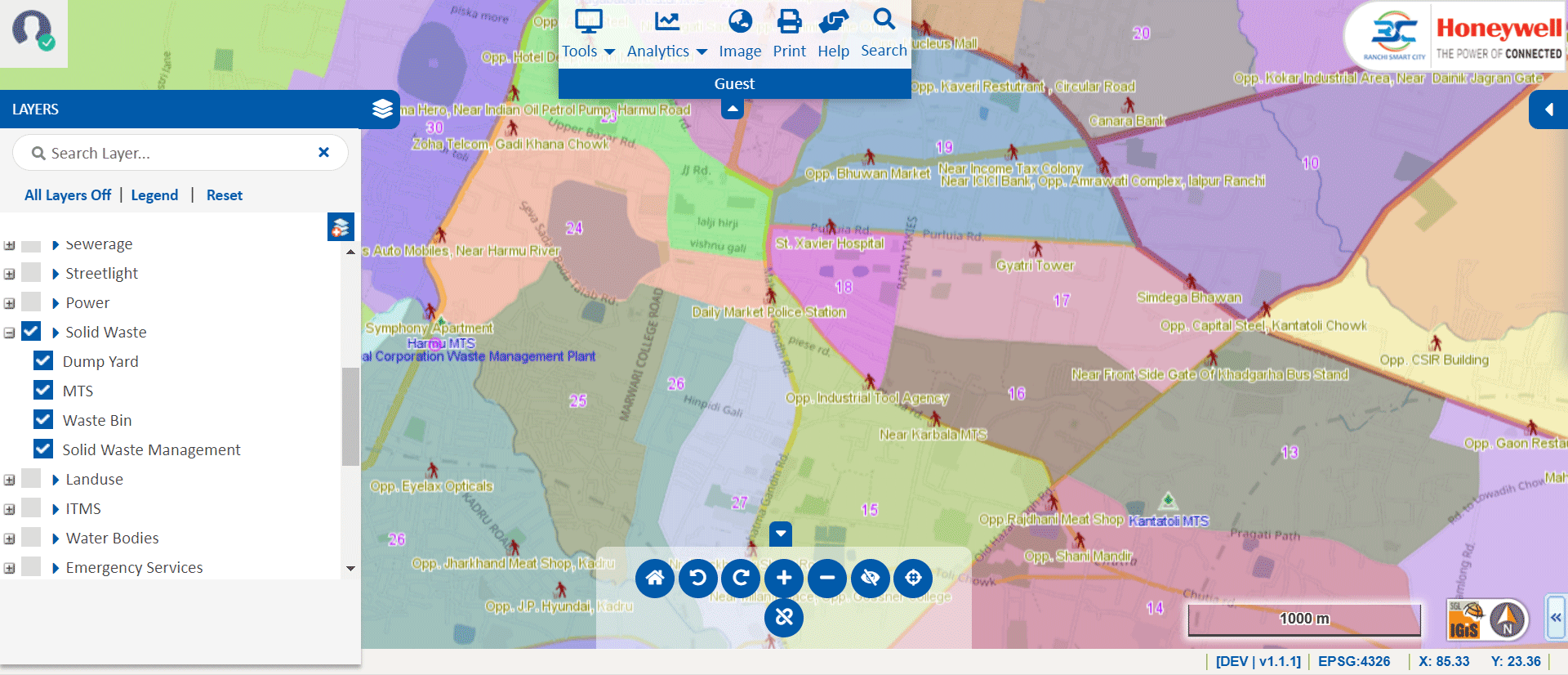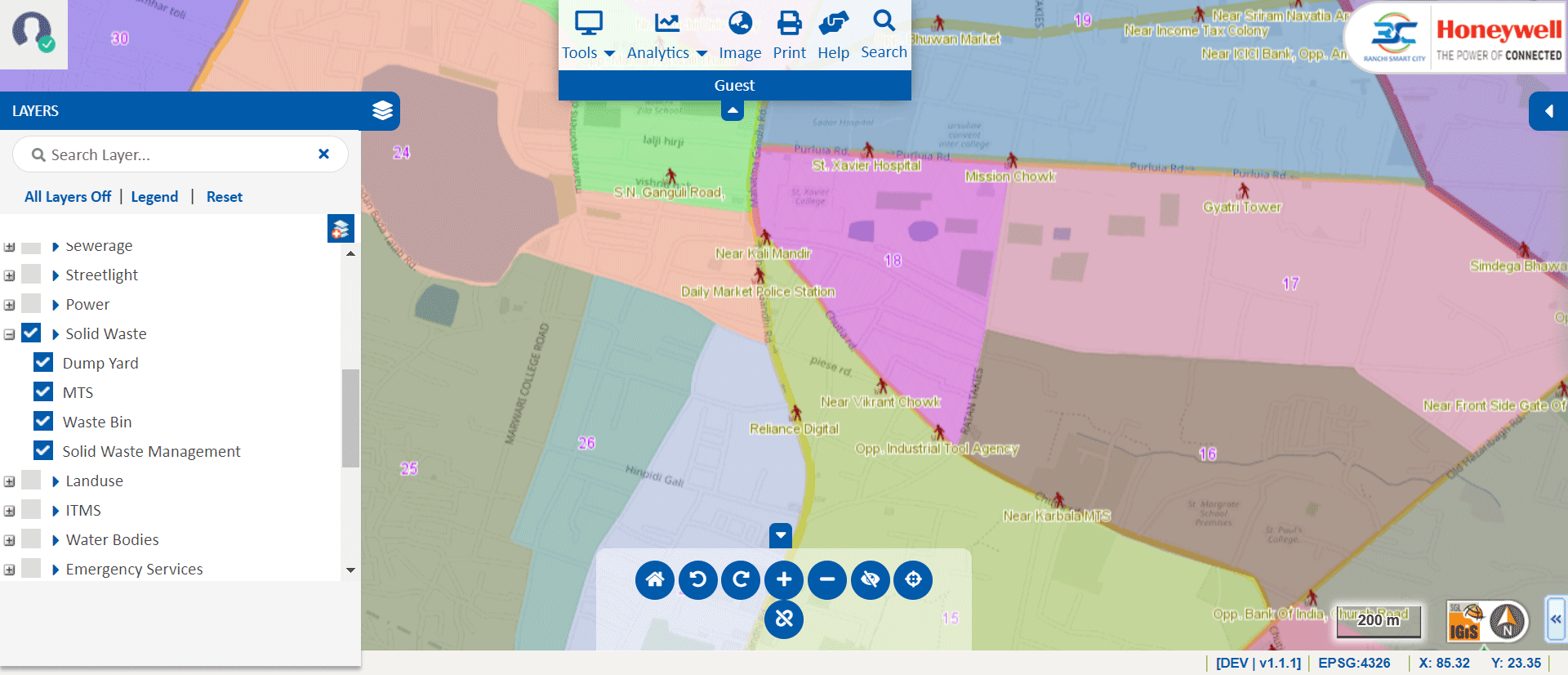
Image Source: Ranchi Smart City – https://gis.rsccl.in/GIS/Home/GISPortal#
» 9. Disaster & Emergency Services Management using GIS
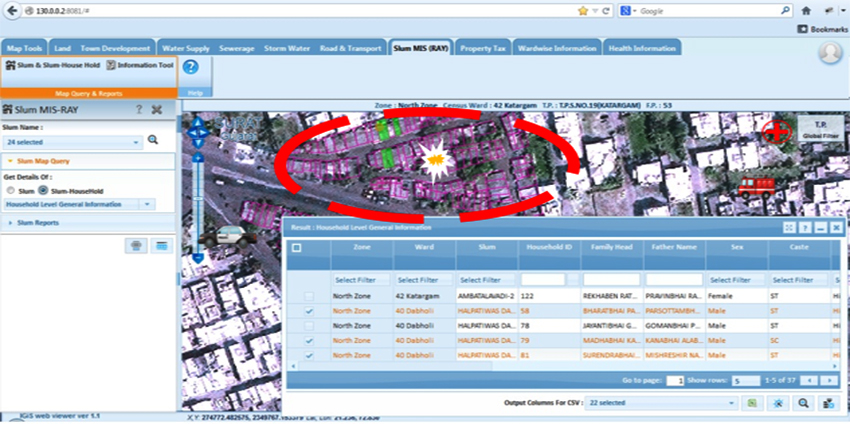
The incredible potential of GIS to benefit the Disaster & Emergency Services Management can be experienced when used. GIS mainly involves the future-based disaster management & mitigation process. Disaster-based complete digital database (Pre-Disaster & post- Disaster) is mapped & displayed to the public to gain awareness about the severity of disasters. Additionally, needy emergency details (where & when) are also mapped. It leads to a safe & secure life for the citizens. From this, city officials can make a plan to mitigate the disaster such as vulnerability site analysis, shortest path, road closures & etc.
The significant GIS applications are listed below in Disaster & Emergency Services Management.
» Identify Disaster Location
» Buffer Affecting Area
» Pull Property Details Mobile No or Mobile tower connected phones
» SMS to disseminate Information on disaster information and remedy or Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for disaster
» Activate Response SOP
» 10. Estate Management using GIS
GIS has the ability to digitally view municipal plot details along with plot dimensions, leading to quick access to information for all. It helps in the proper management of land by highlighting the significant features of a property. In addition, it gives information about slums and the location of ULB (Urban Local Bodies) owned vacant lands & and encroachment, ward boundaries, and so on.
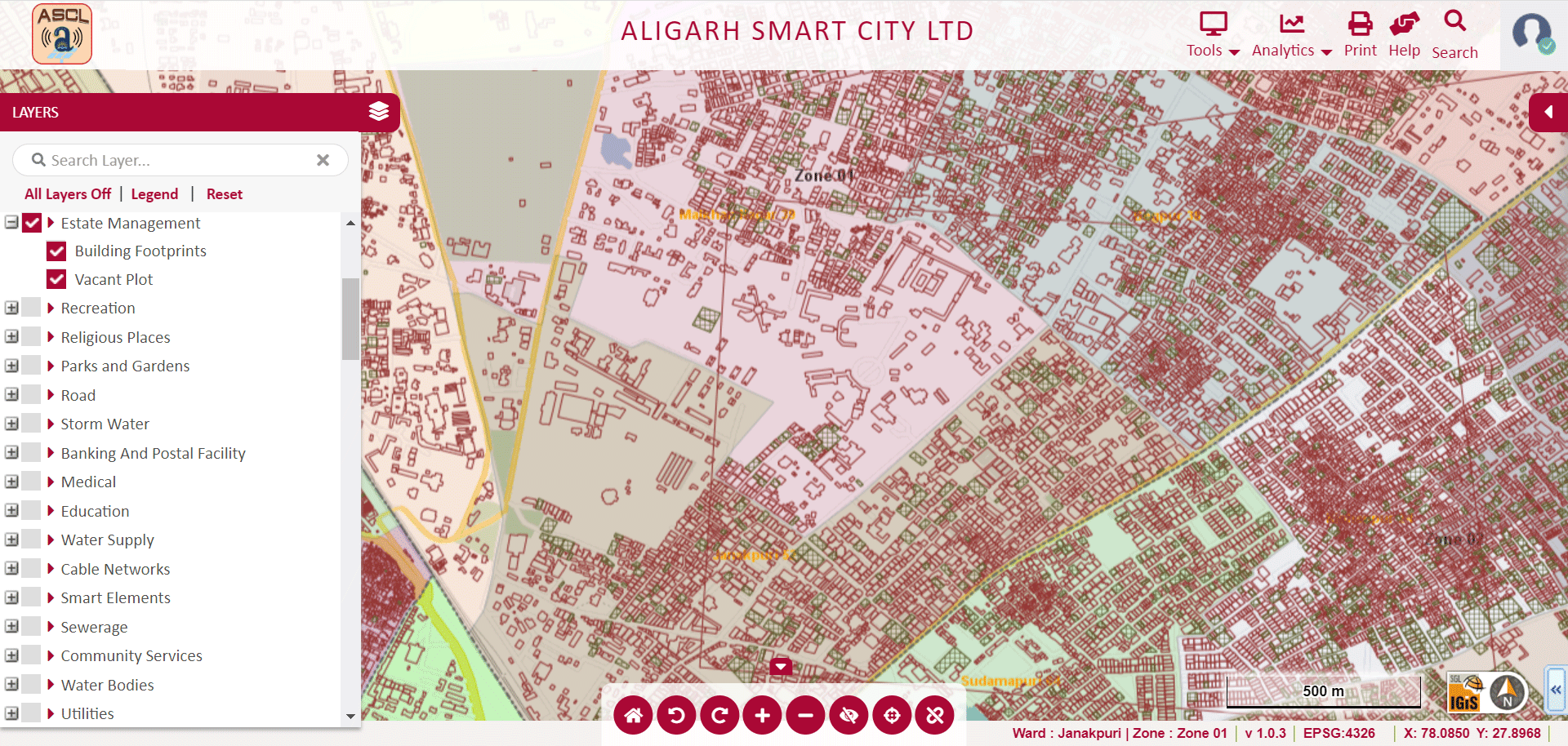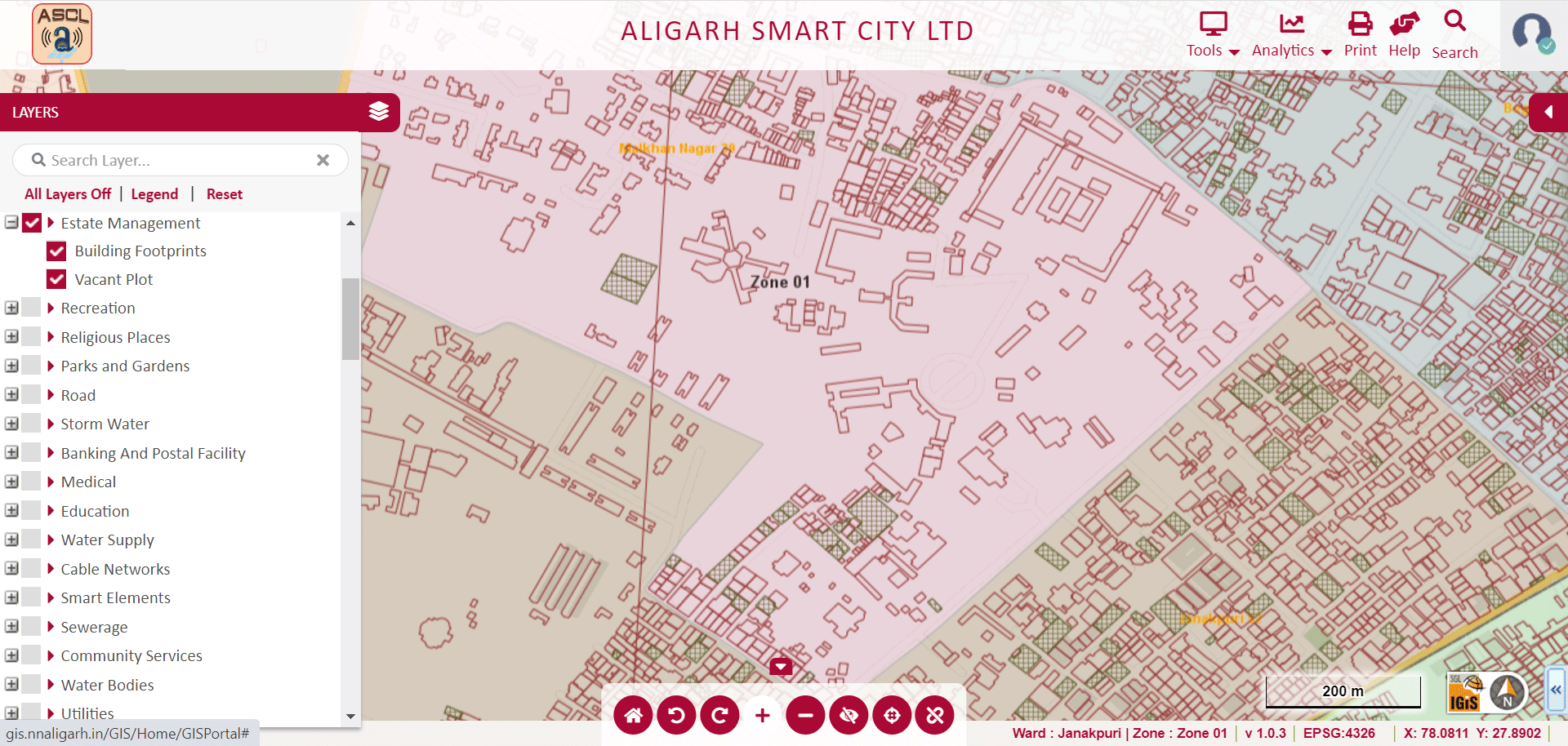
Image Source: Aligarh Smart City – http://gis.nnaligarh.in/GIS/Home/GISPortal#
» Conclusion
Technologies are improving and providing enormous benefits to citizens and governments in a smart city. From well-designed applications of GIS, we can easily conclude that Geospatial Technology plays a crucial role in the journey of cities towards emerging to be smart. A comprehensive digital environment provided by GIS helps to enhance the city systems in terms of pollution abatement, water and waste management, energy optimization, tax and revenue collection, and much more. It continuously improves the lifestyles of citizens through making effective decisions with transparency.
Latest Blog

Smart Waste Management with GIS
1. Introduction: Waste management entails the responsible collection, processing, and disposal of waste materials with a focus on environmental preservation. Its core objectives include waste reduction, resource recovery, and the....
Read More