An Introduction to Remote Sensing and GIS: A Primer for the Novice
There was a discussion among the students about how we can get all the information about our school for the mapping/drawing of our schools. In that, my friend Ram suggested we will measure the building dimensions and note the building color, name, classroom details, and so on. Additionally, Krishna recommended the other details like water tab provision, cycle stand, restroom, and so on. Finally, I suggested google maps. The google map has all the details like our school, our house, our street including our country details.
Ram asked me suddenly, how is it possible to map all the details?
I verbally expressed yes it is possible utilizing remote sensing & GIS (Geographical Information System) technology.
The Remote Sensing, the name itself can easily understand the meaning. It is nothing but getting information from objects without any physical contact with that object but utilizing sensors. Ram was still skeptical of this, I explained further utilizing the example of day-to-day life activity. We are transmuting the Television channels utilizing Television Remote is one example to understand the remote sensing concepts. Similarly, in our body: eyes, ears, and nose are good examples of sensors. These sensors do not physically contact the object but still, we can tell about the physical properties of the object facilely, right? The physical properties are color, size, shape, texture/pattern, and so on. In Remote Sensing, the body is a satellite. The eyes, ears, & nose are different types of sensors to collect variants of data.
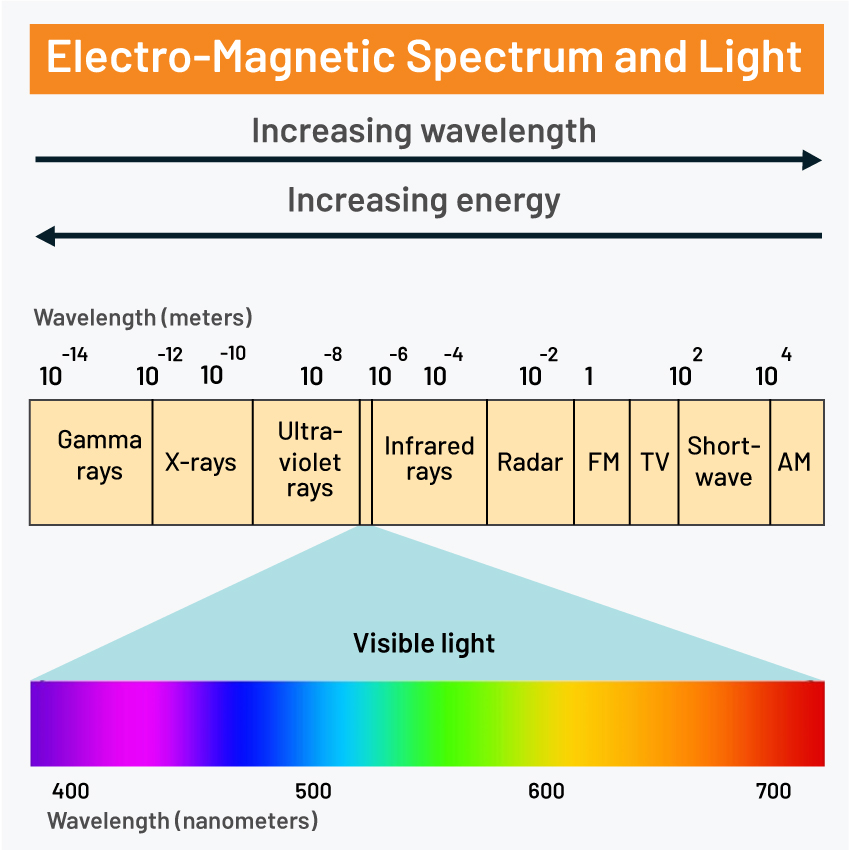
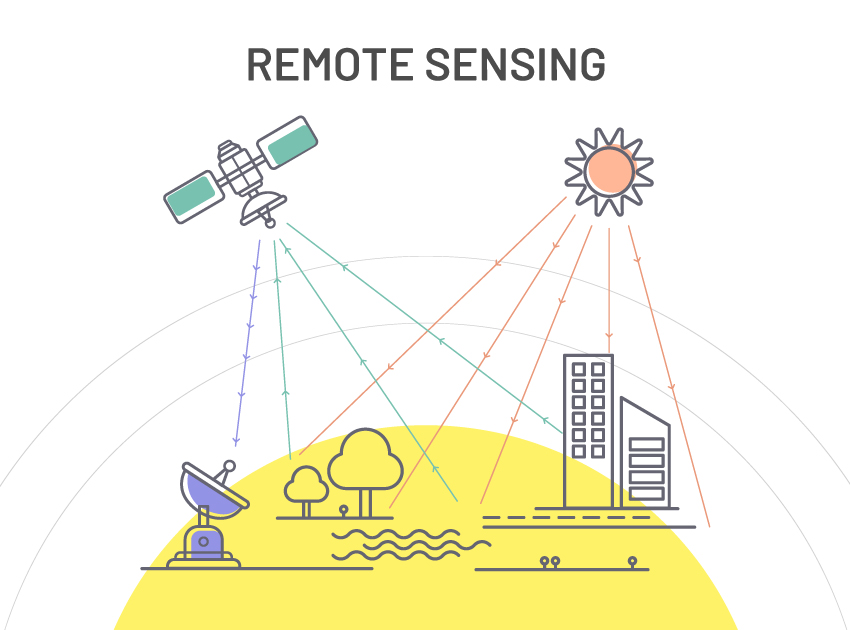
Images of the entire globe are accumulated utilizing Remote Sensing Techniques. Passive and Active sensing systems are available that are used to gather information from any target. Data captured using sunlight or radiated heat is called passive remote sensing. Active remote sensing involves capturing images under external illumination like a flashlight or radar beam.
The energy source for scene illumination is an EMR (Electro-Magnetic Radiation) which has different wavebands like gamma rays, x-rays, ultraviolet rays visible rays, infrared, microwave, and radio waves. Different kinds of sensors are used to collect data in these wave banks.
► Revolution of Remote Sensing and GIS
The collected data was analyzed for different applications. The basic remote sensing data and analysis results along with other geographical data are collectively called geospatial data. A geographical Information System (GIS) is used to process and analyze geospatial data in conjunction with non-spatial data to produce good qualitative & quantitative maps of the earth’s features/global data.
» Remote Sensing
Remote sensing started in the 19th century with the use of film cameras on rudimentary airborne platforms such as hot air balloons, pigeons, and kites to conduct land reconnaissance. The evolution of a new kind of “bird” — the airplane — brought new opportunities in the 1900s, supporting the use of more accurate aerial photography for reconnaissance and mapping.
Satellite technology, launched Remote Sensing into space in the 1970s, supporting the collection of detailed multispectral data that led to an improved understanding of geographic features, urban growth, agriculture, soils & minerals, etc. Multispectral data means images acquired in visible and infrared regions.
» Geographic Information System
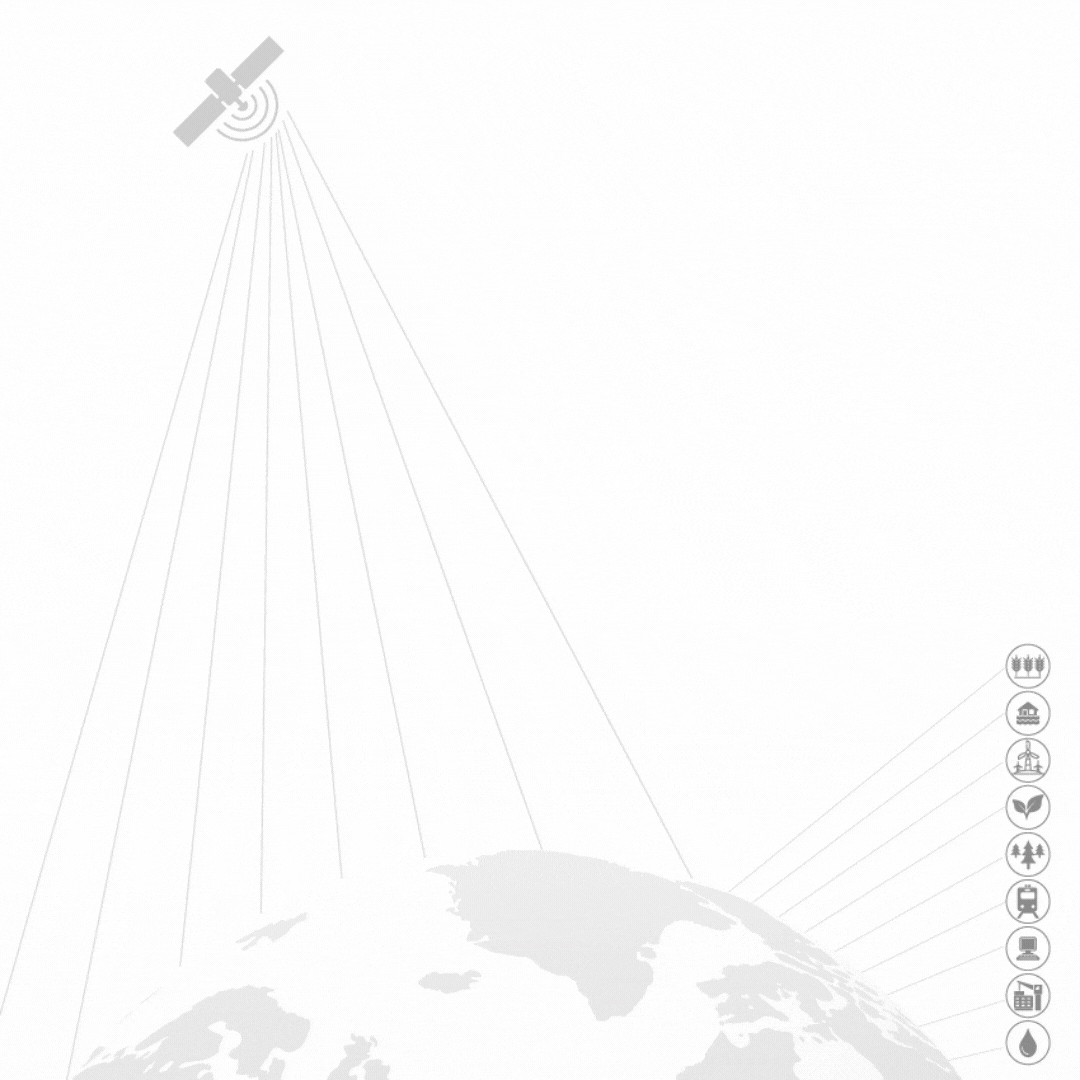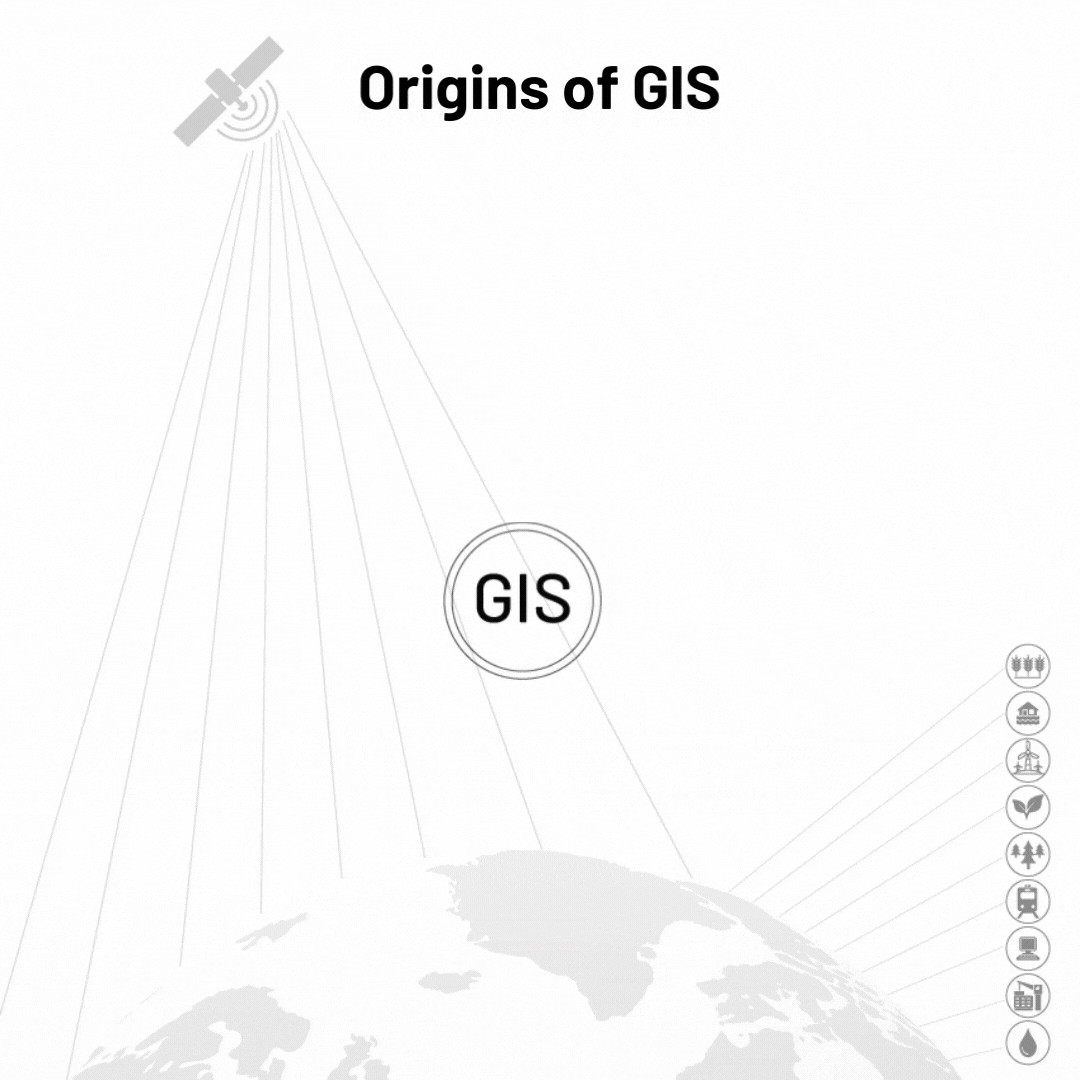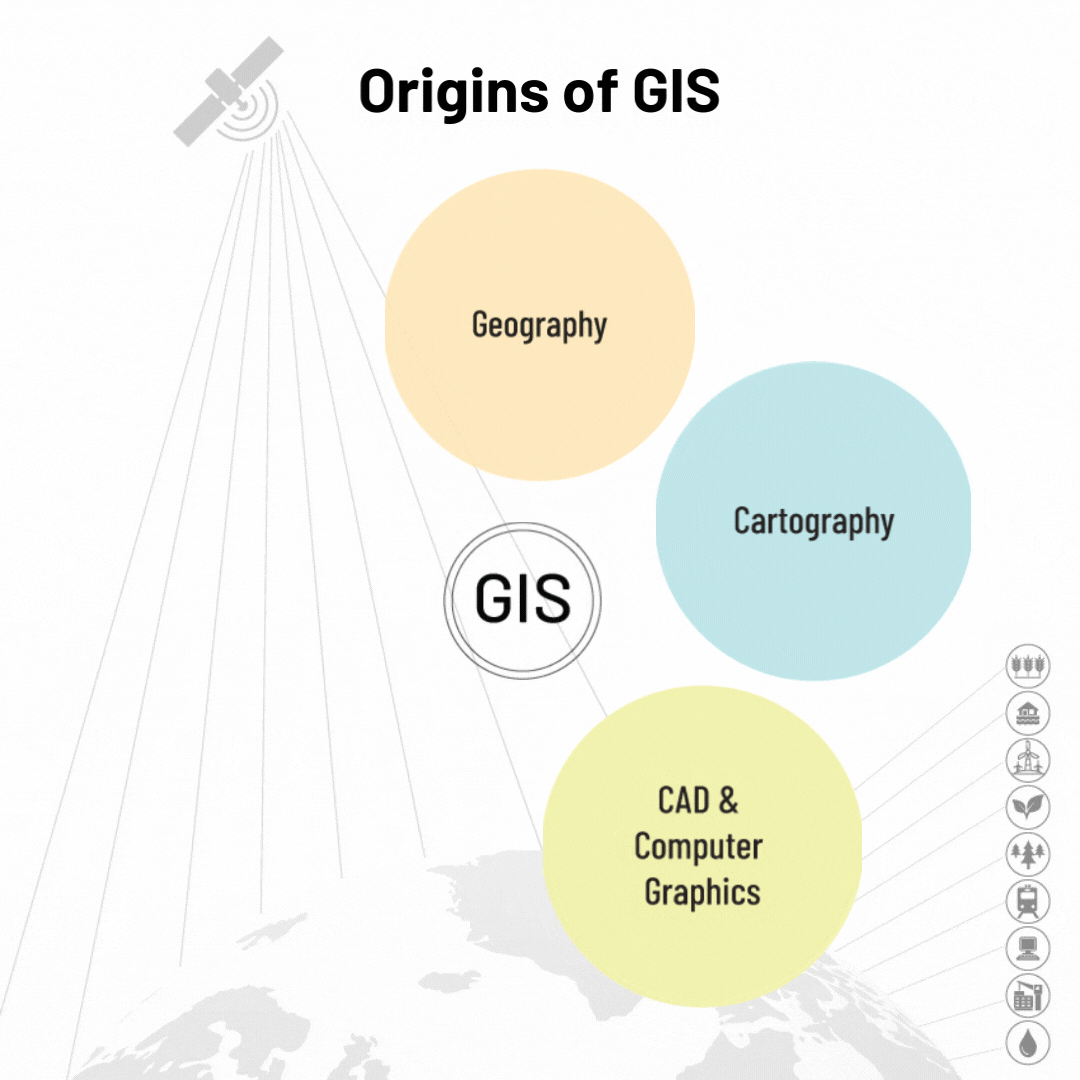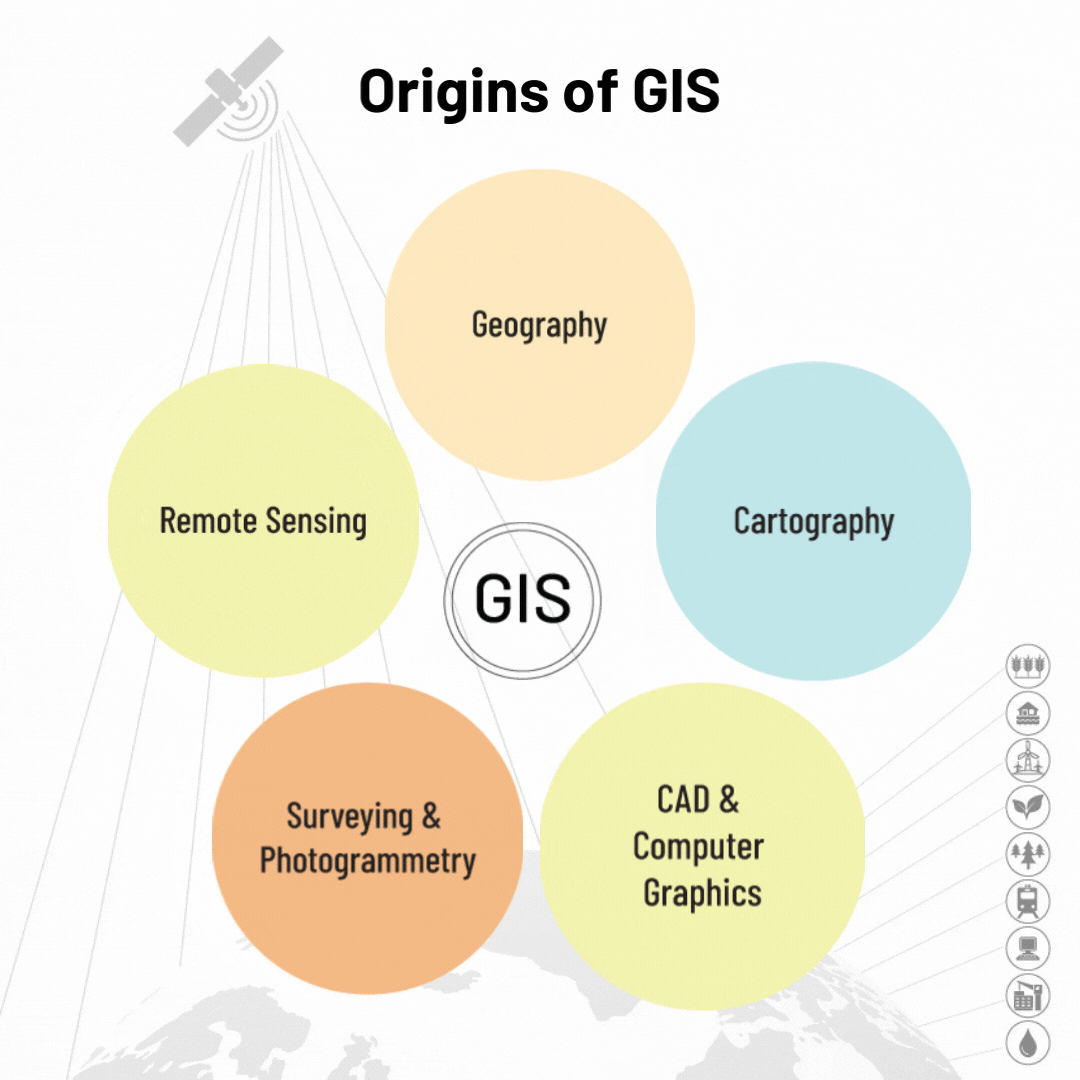
The history of Geographical Information Systems is remarkable and has gone through stages of technology development.
In the 1960s, two applications, SYMAP and GRID, laid out the theoretical foundation for the analysis of raster and vector data, the two main approaches for encoding and storing geographical information. From this moment, GIS evolves through several different periods, thanks to the influence of many external factors. This evolution marks the discipline of GIS itself, the technology it involves, the data, and also the theories and techniques it is built on. Finally, the geographic information is represented as a multilayer map and geospatial visualization to the users. GIS as a science of location has truly evolved from quantitative cartography and geography in the 19th century to map, analyze, and assess real-world problems.
► Development of Remote Sensing and GIS

India’s remote sensing program was developed with the idea of applying space technologies for the benefit of humankind and the development of the country. The program involved the expansion of three principal capabilities. The first was to design sensors for different regions of the EM spectrum and build and launch satellites with these sensors into space for monitoring the earth through a certain path/orbit. The orbit types are many, but the most important are polar orbit and geostationary orbit. A polar orbit satellite meant the satellite path is above or nearly above the poles whereas if the period of the satellite matches the rotation of the Earth, it is called a geostationary orbit. The second was to establish and operate ground stations for spacecraft control, and data transfer along with data processing and archival. The third was to use the data obtained for various applications on the ground.
The GIS allows users to search for information about specific geographical areas, analyze spatial information, edit the data and create maps, charts, and reports that show users the results in visual forms. GIS helps users to find answers to their questions and solve problems by presenting data in simple visual ways.
Robust GIS tools permit organizations to establish and share composite information in ways that users can easily understand. Apart from the governments and public bodies that are major users of GIS, manufacturers and retailers can use GIS to create more efficient supply chains, while health departments can make better-informed decisions about distributing limited resources.
► Advancement of Remote Sensing and GIS
The new technology, i.e., drones and automated robotics techniques will complement traditional airplanes and satellite platforms and deliver more insights than ever before possible. Drones and robots are the latest and most advanced remote sensing platforms catching the eye of the geospatial community. Not only are they cool and cutting-edge, but they also open up a new class of use cases that were previously not possible with traditional aerial survey methods. They offer novel opportunities to monitor remote areas, and their form factors and cost enable a higher frequency of data collection compared to the aerial survey. Remote sensing technology is used in many fields, such as energy, oil and gas, aviation, forestry, transportation, emergency management, and natural resource preservation and restoration.
► Indian Remote Sensing Satellites
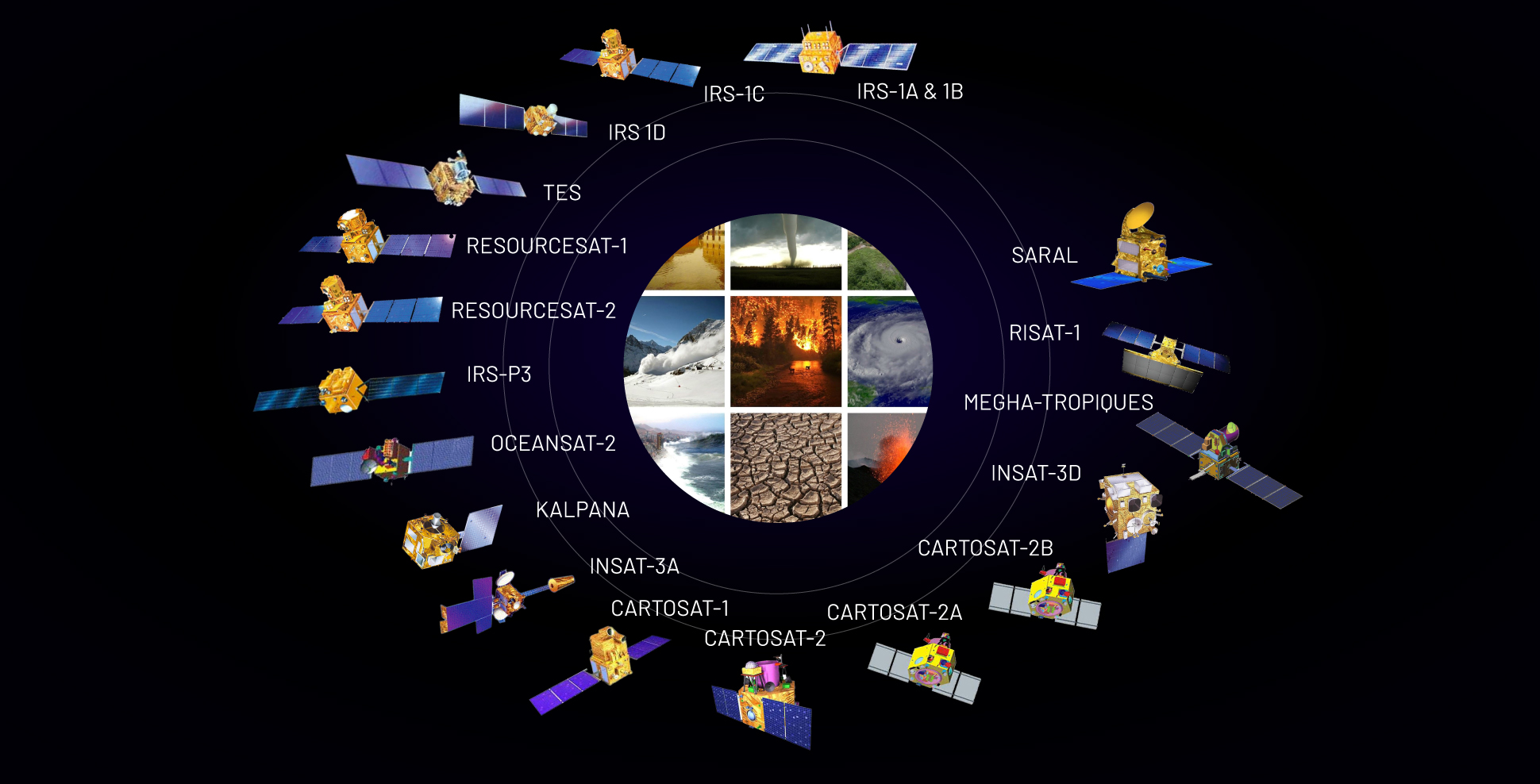
Following the successful demonstration flights of the Bhaskara-1 and Bhaskara-2 satellites launched in 1979 and 1981, respectively, India began to develop the indigenous Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) satellite program to support the national economy in the areas of agriculture, water resources, forestry & ecology, geology, watersheds, marine fisheries & coastal management.
Towards this end, India had established the National Natural Resources Management System (NNRMS) for which the Department of Space (DOS) is the nodal agency, providing operational remote sensing data services. Data from the IRS satellites is received and disseminated by several countries all over the world. With the advent of high-resolution satellites, new applications in the areas of urban sprawl, infrastructure planning and other large-scale applications for mapping have been initiated.
Advancements in Geographical Information Systems (GIS) were the result of several technologies. Databases, computer mapping, remote sensing, programming, geography, mathematics, Computer-Aided Design, and computer science all played a key role in the development of GIS.
Gradually, the importance of spatial analysis for decision-making was becoming recognized. Slowly, GIS was being introduced to classrooms and companies. The software was able to handle both vector and raster data. With more satellites being launched into orbit, this data collected from space could be consumed in a GIS. The evolution of GIS continues, as geospatial systems have transformed along with the increasing power of computers and growing data storage capacity. Tools and techniques are now constantly refined to serve purposes such as urban planning, disaster response, market research, resource management, and military operations.
With open-source mapping and web-based tools/applications like IGiS Enterprise, anyone can get involved in generating data on traffic patterns or the path of a dangerous storm. Creative problem-solvers will continue to push the boundaries of geospatial thinking in the years ahead. There are nearly an unlimited number of applications that are relevant to GIS because virtually all human interactions, natural and man-made features, resources, and populations have a geographic component.
► Why SGL
Remote sensing and Geographic Information Systems are rapidly growing technology and it needs a few processes/analyses to deliver the output as maps or graphs or statistical data. IGiS (Integrated GIS and Image Processing) Software developed by SGL in collaboration with ISRO facilitates image and vector data processing along with newly developed modules like Photogrammetry, and CAD.
► Conclusion
The combination of Remote sensing and GIS is a powerful technology to provide solutions geospatially with accuracy & effectiveness. Remote Sensing makes it possible to collect geographic data from remote areas of the world and even from space in a quick way. The GIS is used to store, edit/manipulate, analyze, integrate, and display the collected geographic data to produce meaningful information such as maps & statistical data in all the domains like agriculture, mineral exploration, urban planning, etc. Remote Sensing and GIS technology are slated for a new era of advances due to the combination of multi-constellation GNSS and 5G technology.
Latest Blog
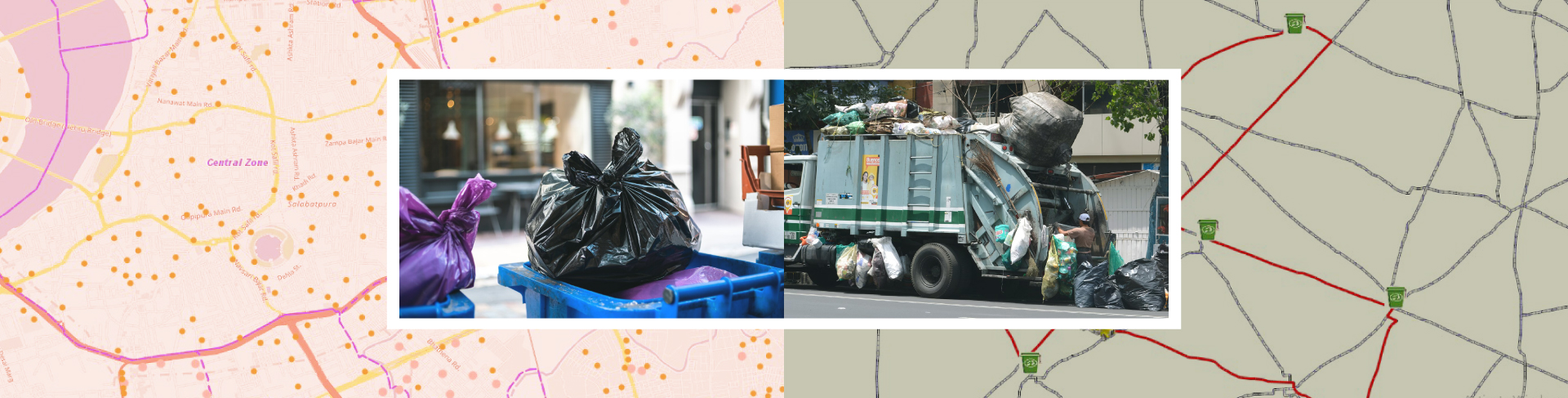

Smart Waste Management with GIS
1. Introduction: Waste management entails the responsible collection, processing, and disposal of waste materials with a focus on environmental preservation. Its core objectives include waste reduction, resource recovery, and the....
Read More